Agri-Food Traceability And Quality Assurance Systems
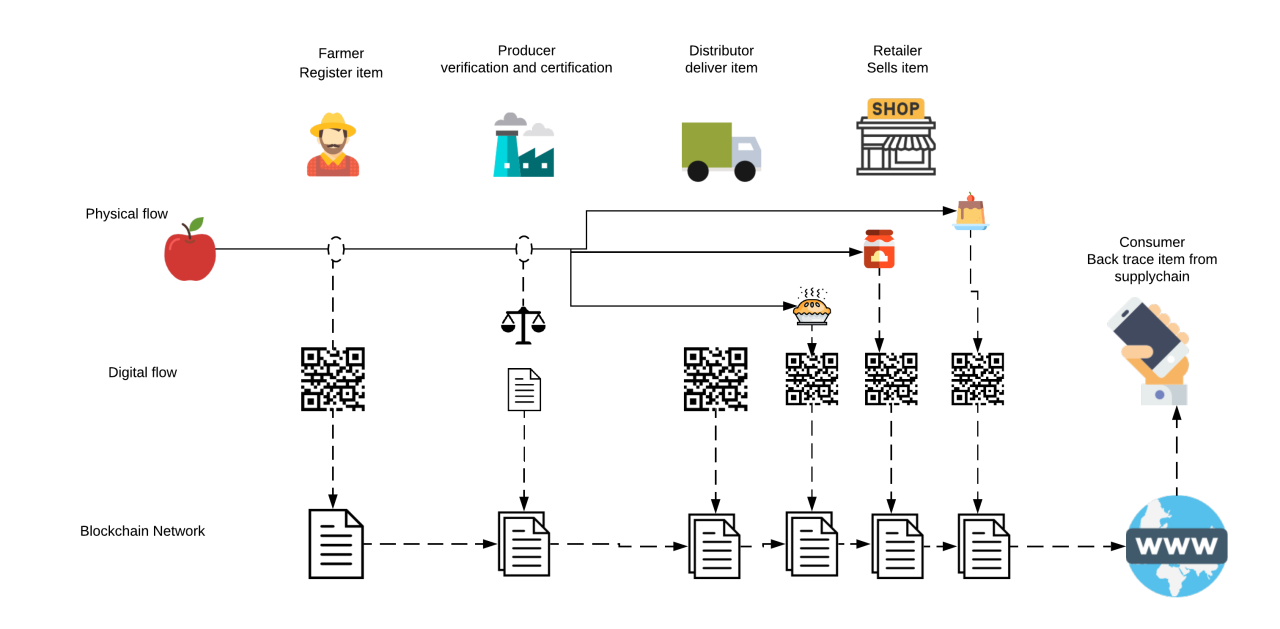
Traceability of Agri-food Supply Chain in Ghana using blockchain
Agriculture plays a crucial role in the development of Ghana's economy. It contributes significantly to the country's GDP and provides employment to a large portion of the population. However, the agri-food supply chain in Ghana faces various challenges such as lack of transparency, inefficient processes, and difficulty in tracing the origin of products. These challenges can be overcome by implementing blockchain technology, which offers a decentralized and transparent system for recording transactions. This article explores how the traceability of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana can be improved using blockchain.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that allows multiple parties to maintain a shared database without the need for a central authority. It provides a secure and transparent way of recording transactions, making it ideal for the agri-food supply chain. By incorporating blockchain into the supply chain, every transaction can be recorded and tracked, ensuring transparency and accountability.
One of the key benefits of using blockchain in the agri-food supply chain is enhanced traceability. Blockchain can enable farmers, suppliers, processors, and retailers to record every transaction related to a product, including its origin, processing methods, and transportation details. This information can then be accessed by consumers, allowing them to verify the authenticity and quality of the product.
Blockchain also improves the efficiency of the supply chain by reducing paperwork and manual processes. With blockchain, all relevant information is recorded digitally, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping and reducing the chances of errors. This streamlines the supply chain and ensures that information is readily available to all stakeholders.
Furthermore, blockchain can help address issues of product counterfeiting and fraud. By recording every transaction on a blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to tamper with the data. This ensures that consumers can trust the authenticity of the products they purchase, reducing the prevalence of counterfeit goods in the market.
What is clear is that blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the agri-food supply chain in Ghana. Its decentralized nature, coupled with its transparency and traceability features, makes it an ideal solution for addressing the challenges currently faced by the sector.
Ideas For Implementing Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain of Ghana
Implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain of Ghana requires careful planning and collaboration among various stakeholders. Here are some ideas for effectively utilizing blockchain in the sector:
1. Establish a Blockchain Consortium
Creating a consortium of key players in the agri-food supply chain, including farmers, suppliers, processors, and retailers, can help facilitate the implementation of blockchain. The consortium can collectively decide on the rules and protocols for recording and accessing data on the blockchain.
2. Develop a Standardized System
To ensure interoperability and seamless integration, it is essential to develop a standardized system for recording and sharing data on the blockchain. This will enable different stakeholders to participate in the system and easily access information. The system should also be user-friendly and accessible to individuals with limited technical knowledge.
3. Provide Training and Education
Blockchain is a relatively new technology, and not all stakeholders may be familiar with its workings. Providing training and education sessions on blockchain technology can help stakeholders understand its benefits and how to effectively utilize it in the agri-food supply chain. This will promote adoption and ensure that all participants are equipped with the necessary skills.
4. Pilot Projects
Before implementing blockchain on a large scale, conducting pilot projects can help identify any challenges or issues that may arise. These projects can be carried out in specific regions or with specific products to test the effectiveness and practicality of using blockchain in the agri-food supply chain.
Recommendations for Implementing Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain of Ghana
While implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain of Ghana holds great potential, it is essential to consider certain recommendations to ensure successful and effective adoption:
1. Collaboration and Cooperation
Implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain requires collaboration and cooperation among all stakeholders. It is crucial to involve farmers, suppliers, processors, retailers, and regulatory bodies to ensure the smooth implementation of blockchain technology.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Blockchain solutions should be scalable and flexible to accommodate the growing demands of the agri-food supply chain. As the sector expands, the blockchain infrastructure should be able to handle increased transactions and data volumes without compromising on speed and efficiency.
3. Security and Privacy
As blockchain involves recording sensitive data, it is essential to prioritize security and privacy. Implementing robust security measures and ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to specific information will help build trust and confidence in the system.
4. Government Support
The government should play an active role in supporting the adoption of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain. This can be done through providing financial incentives, creating regulatory frameworks, and promoting awareness of blockchain technology among farmers and other stakeholders.
Listicle of Benefits of Using Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits when applied to the agri-food supply chain. Here are some key advantages:
1. Transparency
Blockchain provides a transparent and immutable record of every transaction in the supply chain. This enables consumers to verify product origin, quality, and authenticity.
2. Traceability
With blockchain, every transaction related to a product can be traced back to its origin, providing visibility into the entire supply chain. This helps in identifying and addressing issues such as contamination or non-compliance with standards.
3. Efficiency
By eliminating manual processes and paperwork, blockchain streamlines the supply chain and reduces the chances of errors. This improves overall efficiency and reduces costs.
4. Security
Blockchain's decentralized and tamper-proof nature enhances security within the agri-food supply chain. It reduces the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
5. Trust and Confidence
Blockchain builds trust and confidence among consumers by providing a transparent and trustworthy system for recording transactions. It allows consumers to make informed choices based on reliable information.
Question & Answer
Q: How does blockchain ensure the transparency of the agri-food supply chain?
A: Blockchain provides a decentralized and transparent system for recording transactions. Every transaction related to a product in the supply chain is recorded on the blockchain, allowing consumers to verify its origin and quality.
Q: Can blockchain help reduce product counterfeiting?
A: Yes, blockchain can help reduce product counterfeiting by providing a tamper-proof record of every transaction. This ensures that consumers can trust the authenticity of the products they purchase.
Q: What are some challenges in implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain?
A: Some challenges include the need for collaboration among stakeholders, scalability of the system, ensuring security and privacy, and providing training and education on blockchain technology.
Q: How can blockchain improve the efficiency of the agri-food supply chain?
A: By eliminating manual processes and paperwork, blockchain reduces the chances of errors and streamlines the supply chain. This improves overall efficiency and reduces costs.
Summary of Using Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain of Ghana
Implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain of Ghana has the potential to overcome various challenges faced by the sector. By providing transparency, traceability, efficiency, security, and trust, blockchain can revolutionize the way transactions are recorded and tracked in the supply chain. However, successful implementation requires collaboration among stakeholders, scalable and flexible solutions, prioritizing security and privacy, and government support. By effectively utilizing blockchain, Ghana can establish a robust and reliable agri-food supply chain that benefits all participants.

Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Traceability And Quality Assurance Systems"