Agroecology Regenerative Farming For Sustainable Food Systems
Agroecology plays a crucial role in sustainable agricultural practices, offering a promising framework that integrates ecological principles with agricultural production. With growing concerns about the environmental impacts of conventional farming methods, agroecology has emerged as a viable alternative that promotes biodiversity, soil health, and resilient food systems. In this post, we will explore the concept of agroecology, its potential benefits, and recommendations for its widespread adoption.
But first, let's take a moment to appreciate the image below:
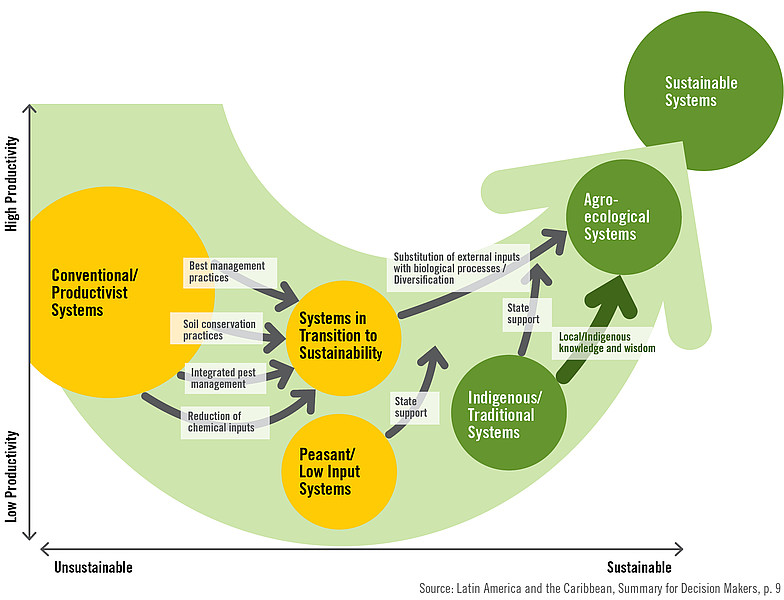
What is Agroecology?
Agroecology can be defined as the study of ecological processes applied to agricultural systems. It recognizes the interdependence between plants, animals, humans, and the environment, emphasizing the importance of ecological balance in farming practices. Unlike conventional agriculture, which relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, agroecology aims to create self-sustaining agricultural ecosystems that mimic natural processes.
Ideas For Implementing Agroecology:
1. Diversifying Crop Production:
Agroecology encourages farmers to cultivate a wide variety of crops, promoting biodiversity and reducing the risk of crop failure due to pests or diseases. Crop rotations, polycultures, and intercropping are some strategies that can enhance resilience and improve soil fertility.
2. Integrating Livestock:
Combining livestock with crop production allows for nutrient cycling and reduces the dependence on synthetic fertilizers. Integrating animals such as chickens or goats into farming systems can help control pests and weeds naturally, while their manure provides valuable organic matter for the soil.
3. Conservation Agriculture:
Conservation agriculture practices, including minimal soil disturbance, the use of cover crops, and the maintenance of permanent soil cover, help prevent erosion, conserve water, and enhance soil health. By implementing these practices, farmers can improve the long-term sustainability of their operations.
4. Water Management Techniques:
Efficient water management is a crucial aspect of agroecology. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and the use of agroforestry systems can help conserve water resources and ensure irrigation practices are more precise and sustainable.
Recommendations For Embracing Agroecology:
1. Building Knowledge and Capacity:
Empowering farmers with knowledge about agroecological practices is essential for their successful adoption. Governments, NGOs, and agricultural institutions should invest in training programs and workshops to equip farmers with the necessary skills and understanding to implement agroecology effectively.
2. Promoting Policy Support:
Developing policies that incentivize and support agroecological practices is crucial. Governments should provide financial support, subsidies, and technical assistance to farmers who adopt agroecology, creating a conducive environment for its widespread implementation.
3. Facilitating Knowledge Exchange:
Encouraging knowledge exchange platforms, such as farmer-to-farmer networks, online forums, and interactive workshops, can foster collaboration and provide a space for farmers to share their experiences, challenges, and success stories related to agroecology.
4. Investing in Research and Development:
Investment in research and development is necessary to continually improve agroecological practices. Researchers should explore innovative techniques, crop varieties, and pest management strategies that align with the principles of agroecology to facilitate its adoption and enhance its effectiveness.
Listicle of Benefits Provided by Agroecology:
- Promotes biodiversity and conservation of natural resources
- Reduces dependence on synthetic inputs
- Enhances soil health and fertility
- Improves resilience to climate change
- Ensures food security and sovereignty
- Involves local communities in decision-making processes
- Supports rural livelihoods and social equity
- Minimizes negative impacts on ecosystems and human health
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and mitigates climate change
- Creates sustainable and resilient food systems
Question & Answer:
Q: Does agroecology only apply to small-scale farming?
A: Not at all. While agroecology is often associated with small-scale farming, its principles can be applied to various types and scales of agricultural systems. Many large-scale farms have successfully incorporated agroecological practices into their operations, demonstrating that it is feasible to adopt these methods in different contexts.
Q: Can agroecology help address food insecurity?
A: Absolutely. Agroecology focuses not only on sustainable agricultural practices but also on ensuring food security and sovereignty. By promoting diverse and resilient farming systems, agroecology can contribute to increased food production, improved nutrition, and enhanced livelihoods, particularly in regions with limited access to food.
Summary of Agroecology:
Agroecology offers a holistic approach to agriculture that integrates ecological principles into farming practices. By embracing diversity, reducing chemical inputs, conserving resources, and prioritizing the well-being of ecosystems and communities, agroecology holds great promise for building sustainable and resilient food systems. Governments, institutions, and farmers must work together to embrace and promote agroecology, unleashing its potential to transform our agricultural landscape and secure a more sustainable future.
And there we have it, a comprehensive exploration of agroecology and its potential for revolutionizing our agricultural systems. Let's embrace this innovative approach and work towards a more sustainable future.

Post a Comment for "Agroecology Regenerative Farming For Sustainable Food Systems"