Organic Certification And Standards For Trustworthy Farming Practices
Organic farming is gaining popularity worldwide due to its numerous benefits for both our health and the environment. The process of organic certification ensures that farmers adhere to strict guidelines and practices to produce food without the use of synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms. In this article, we will explore the steps involved in the organic certification process for farming, as outlined by the Irish Organic Association.
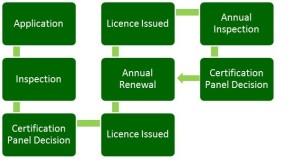
1. Application:
The first step towards obtaining organic certification is to submit an application to the certification body. This application includes detailed information about the farm, such as the types of crops or livestock involved, the land area, and any previous use of chemicals on the land.
2. Inspection:
Once the application is received, the certification body will conduct an on-site inspection of the farm. This inspection helps ensure that all organic farming practices are being followed. The inspector assesses various aspects, including soil management, pest control methods, and animal welfare.
3. Conversion Period:
Before receiving certification, a conversion period is required. This period allows for any residual chemicals or substances in the soil to break down naturally. Generally, the conversion period is around two years, during which the farmer must strictly adhere to organic farming practices.
4. Documentation:
Throughout the certification process, the farmer is required to maintain detailed records of all activities on the farm. This documentation serves as evidence that the established organic guidelines are being followed. It includes records of crop rotations, pest control measures, and any inputs used, such as fertilizers or compost.
5. Assessment:
Based on the inspection report and the documentation provided, the certification body thoroughly reviews all information to determine whether the farm meets the organic certification requirements. This assessment involves a meticulous evaluation of the farmer's practices and adherence to organic standards.
6. Certification Decision:
After the assessment, the certification body makes a decision regarding organic certification. If the farm successfully meets all the criteria and standards, the farmer is granted certification. A certificate is issued, acknowledging that the farm is authorized to sell organic produce.
7. Annual Renewal:
Organic certification is not a one-time process. Farmers must renew their certification on an annual basis. This renewal includes a new inspection, assessment, and documentation review to ensure compliance with organic farming practices is maintained.
8. Marketing and Labeling:
Once certified, farmers can market their products as organic. They are allowed to use specific organic labels on their packaging, which provides consumers with an assurance that the product has been produced using organic farming methods.
9. Regular Inspections:
Throughout the certification period, regular inspections are conducted by the certification body to ensure ongoing compliance with organic standards. These inspections help maintain the integrity and credibility of organic farming practices.
10. Continuous Improvement:
Organic farming is an ongoing learning process. Farmers are encouraged to continuously improve their practices to enhance the sustainability and organic quality of their produce. They can stay updated on the latest organic farming techniques and innovations through workshops, training programs, and networking with other organic farmers.
What is Organic Certification?
Organic certification is a process that ensures agricultural products are grown and processed according to specific organic standards. These standards prohibit the use of synthetic chemicals, fertilizers, genetically modified organisms, and irradiation in farming practices. Organic certification provides consumers with confidence that the products they purchase are truly organic and have been produced in an environmentally and socially responsible manner.
Ideas For Organic Farming
1. Crop Rotation:
Implementing a crop rotation system helps maintain soil fertility, reduces pest and disease pressure, and minimizes soil erosion. This practice involves growing different crops in a specific sequence, which helps break pest and disease cycles and improves soil health.
2. Composting:
Composting organic waste, such as crop residues, animal manure, and kitchen scraps, provides a rich source of nutrients for plants. Using compost as a natural fertilizer improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and promotes healthy plant growth.
3. Biological Pest Control:
Encouraging natural predators and beneficial insects in the field helps control pests organically. Ladybugs, lacewings, and predatory mites are examples of beneficial insects that can effectively prey on pests, reducing the need for chemical insecticides.
4. Cover Crops:
Planting cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, during fallow periods helps protect the soil from erosion, suppresses weed growth, and improves soil fertility. Cover crops also increase organic matter content, which enhances soil structure and provides nutrients for future crops.
5. Water Conservation:
Efficient water management is crucial in organic farming. Techniques such as drip irrigation, mulching, and rainwater harvesting help conserve water, reduce soil erosion, and promote healthy plant growth.
Recommendations For Organic Farmers
1. Stay Informed:
Keep up-to-date with organic standards, regulations, and best practices in organic farming. Attend workshops, seminars, and conferences to gain knowledge about the latest advancements in organic agriculture.
2. Networking:
Connect with other organic farmers, join organic farming associations or groups, and participate in farmer's markets. Networking with like-minded individuals provides opportunities to share experiences, exchange ideas, and learn from each other.
3. Soil Testing:
Regularly test soil for nutrient levels, pH balance, and organic matter content. Soil testing helps identify any deficiencies or imbalances, allowing farmers to make informed decisions when applying organic fertilizers or amendments.
4. Crop Diversity:
Plant diverse crops on the farm to promote biodiversity and reduce the risk of pests and diseases. Different crops attract different insects and microorganisms, creating a more balanced ecosystem.
5. Optimize Resources:
Efficient resource management, including water, energy, and nutrients, is essential in organic farming. Minimize waste and explore sustainable practices such as rainwater harvesting, renewable energy sources, and efficient irrigation systems.
Listicle of Organic Farming Benefits
1. Health Benefits:
- Organic food is free from synthetic chemicals, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms, making it healthier for consumers.
- Organic farming practices promote nutrient-rich soil, resulting in more nutritious crops.
- Reduced exposure to harmful chemicals may lead to lower health risks, such as hormone disruption and pesticide residues.
2. Environmental Benefits:
- Organic farming reduces soil erosion and improves soil health by promoting organic matter content.
- Eliminating synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms supports biodiversity and protects ecosystems.
- Organic farming practices prioritize water conservation and reduce pollution of water bodies due to the absence of chemical runoff.
3. Sustainability:
- Organic farming emphasizes sustainable practices such as crop rotation, composting, and natural pest control.
- By avoiding synthetic chemicals, organic farming reduces the carbon footprint associated with conventional agriculture.
- Organic farms often prioritize animal welfare, providing animals with access to pasture and avoiding the use of growth hormones or antibiotics.
Question & Answer
Q: Can organic farmers use any kind of fertilizer?
A: Organic farmers primarily use natural fertilizers, such as compost, manure, and bone meal. These fertilizers provide a slow release of nutrients and improve soil structure over time.
Q: Is organic farming more expensive than conventional farming?
A: Initially, organic farming may require higher investments due to the additional labor involved and the cost of organic fertilizers. However, the long-term benefits, such as increased soil fertility and reduced health risks, outweigh the initial costs.
Q: Can organic farmers use pesticides?
A: Organic farmers use natural pest control methods, such as biological controls, crop rotation, and companion planting, to manage pests. However, in cases of severe infestations, organic-approved pesticides derived from natural sources may be used as a last resort.
Summary of Organic Certification Process
The process of organic certification for farming involves multiple steps to ensure that farmers adhere to strict organic standards and farming practices. Applying for certification, undergoing inspections, maintaining detailed records, and undergoing annual renewals are critical aspects of the certification process. Organic farming offers a range of benefits, including improved human health, environmental conservation, and the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices. By choosing organic products, consumers can support farmers who prioritize health, sustainability, and environmental responsibility.

Post a Comment for "Organic Certification And Standards For Trustworthy Farming Practices"