Agroecological Farming And Climate Change Mitigation
Climate change, soil degradation, and land management are pressing issues that demand urgent attention. It is crucial to address these challenges through sustainable practices, taking into account their impacts on future generations. In this post, we will explore the importance of sustainable soil and land management in the context of climate change.
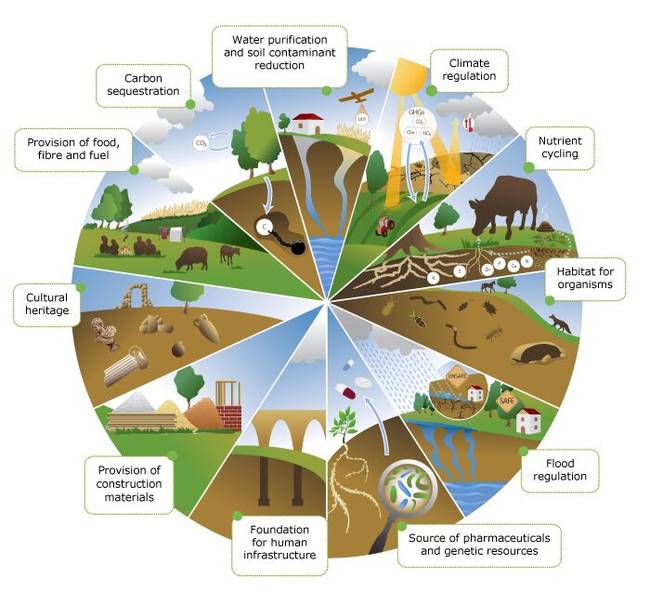
As we face the consequences of climate change, it becomes increasingly apparent that sustainable soil and land management is key to mitigate its effects. The degradation of soil and mismanagement of land contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating the climate crisis.
One of the most effective ways to combat climate change is through sustainable soil and land management practices. By implementing these practices, we can enhance carbon sequestration, improve soil fertility, and reduce the risk of land degradation.
But what exactly is sustainable soil and land management? It involves using practices that maintain or enhance soil health, prevent soil erosion, conserve water resources, and promote biodiversity. These practices include conservation agriculture, agroforestry, organic farming, and integrated pest management, among others.
Conservation agriculture, for example, focuses on reducing soil disturbance, maintaining soil cover, and diversifying crop rotations. By adopting this approach, farmers can improve soil structure, increase water infiltration, reduce erosion, and enhance nutrient cycling.
Agroforestry is another practice that integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural systems. By doing so, it provides shade, improves soil fertility, and sequesters carbon. Agroforestry systems also promote biodiversity, offering habitats for various species and enhancing ecosystem services.
Organic farming, with its emphasis on avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, protects soil health and biodiversity. It relies on natural inputs and biological processes, thereby reducing negative environmental impacts and providing consumers with healthier food options.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is a holistic approach to pest control that aims to minimize the use of pesticides. IPM utilizes a combination of techniques such as biological control, crop rotation, and habitat modification to manage pests effectively while preserving soil health.
Implementing sustainable soil and land management practices requires knowledge sharing, technical support, and policy interventions. It is crucial to involve farmers, researchers, policy-makers, and stakeholders in collaborative efforts to scale up these practices.
What is the role of governments in promoting sustainable soil and land management?
Governments play a vital role in creating an enabling environment for sustainable soil and land management. They can implement policies that incentivize sustainable practices and provide support to farmers to adopt these practices.
Additionally, governments can invest in research and innovation to develop new technologies and practices that mitigate the impacts of climate change on soil and land. This can involve funding scientific studies, establishing knowledge-sharing platforms, and creating networks of experts.
Ideas for promoting sustainable soil and land management:
1. Provide financial incentives to farmers who adopt sustainable practices.
2. Offer technical assistance to farmers to implement sustainable soil and land management techniques.
3. Conduct awareness campaigns to educate farmers and the general public about the importance of sustainable practices.
4. Develop training programs for agricultural professionals on sustainable soil and land management.
5. Create platforms for knowledge exchange and collaboration among farmers, researchers, and policymakers.
Recommendations for policymakers:
1. Integrate sustainable soil and land management practices into national climate change strategies.
2. Encourage the inclusion of sustainable practices in agricultural policies and programs.
3. Establish monitoring systems to track the adoption and effectiveness of sustainable soil and land management practices.
4. Collaborate with international organizations and partners to share best practices and experiences.
5. Allocate sufficient funding for research and development in sustainable soil and land management.
Listicle of benefits of sustainable soil and land management practices:
1. Increased soil fertility and nutrient availability for crops.
2. Improved water infiltration and retention, reducing irrigation needs.
3. Enhanced carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change.
4. Reduced erosion and land degradation, preserving valuable agricultural land.
5. Preservation of soil biodiversity and ecosystem services.
6. Healthier food options through organic farming practices.
7. Conservation of water resources and protection of aquatic ecosystems.
8. Resilience to extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods.
9. The establishment of diverse habitats that support biodiversity.
10. Improved livelihoods and economic opportunities for farmers through sustainable agricultural practices.
Question & Answer:
Q: How can sustainable soil and land management contribute to climate change mitigation?
A: Sustainable soil and land management practices increase carbon sequestration, which means that more carbon dioxide is stored in the soil instead of being released into the atmosphere. This helps to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Q: Are sustainable soil and land management practices cost-effective for farmers?
A: While implementing sustainable practices may require initial investments, they can lead to long-term cost savings. For example, reduced fertilizer and pesticide use in organic farming can lower input costs, and improved soil health can enhance crop productivity.
Summary of sustainable soil and land management:
Sustainable soil and land management practices are essential for addressing the challenges posed by climate change. By adopting and promoting these practices, we can enhance soil fertility, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and protect valuable land resources. Governments, farmers, researchers, and policymakers must work together to scale up sustainable soil and land management efforts and create a sustainable future for generations to come.
Post a Comment for "Agroecological Farming And Climate Change Mitigation"