Agroecosystem Restoration For Biodiversity Conservation
Hey there! Today, I want to talk to you about an important topic that affects our environment and food production: soil. Soil plays a pivotal role in supporting plant growth and providing essential nutrients for crops. Unfortunately, soil degradation has become a significant issue that needs our attention. In this post, we will explore how we can restore soil functions and agroecosystem services to promote a sustainable future.
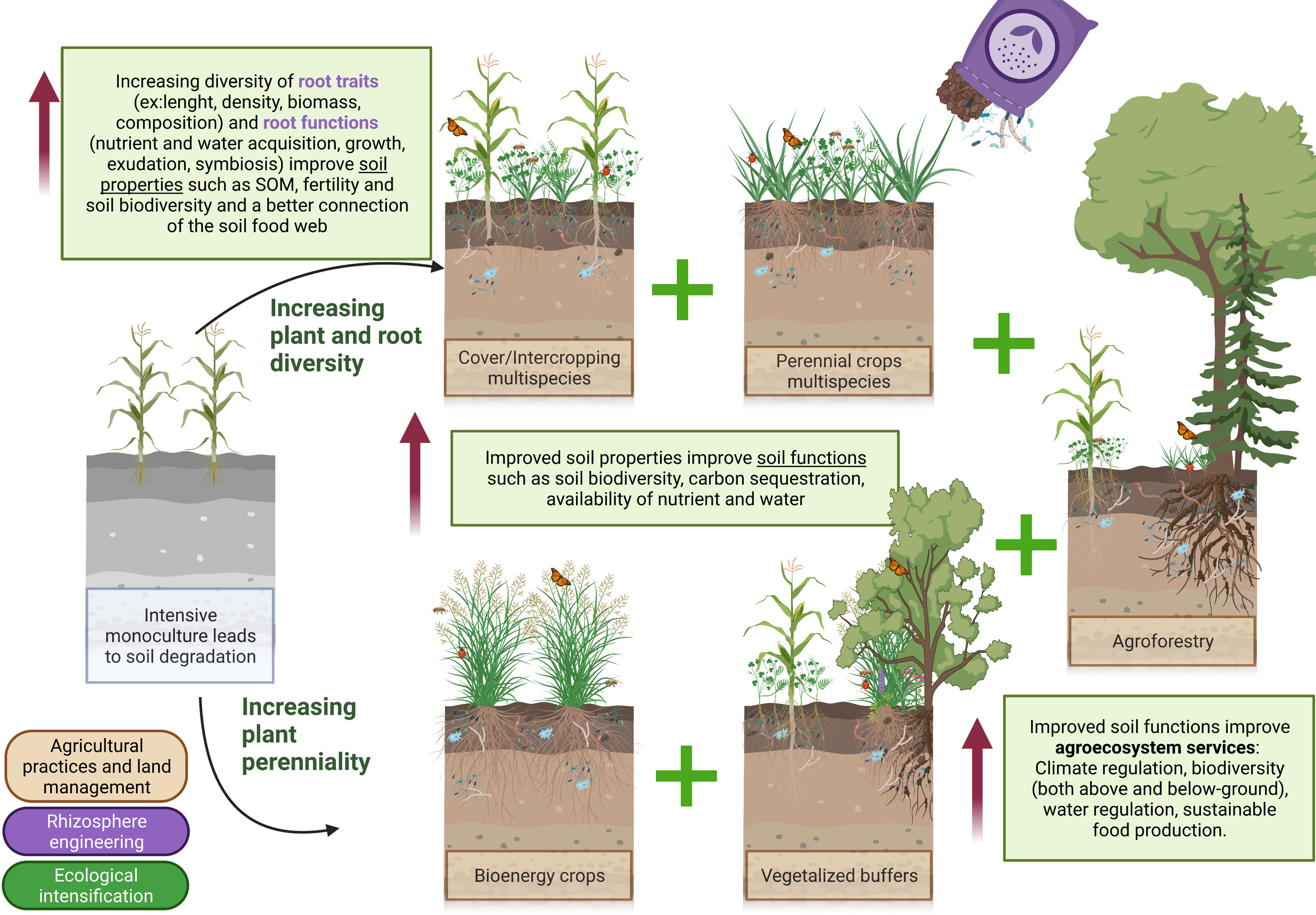
So, what exactly are soil functions and agroecosystem services? Soil functions refer to the natural processes that occur within the soil, such as nutrient cycling, water filtration, and carbon sequestration. Agroecosystem services, on the other hand, are the benefits we derive from the soil in terms of food production, biodiversity conservation, and climate regulation.
Now that we understand the importance of soil, let's delve into some ideas for restoring soil functions and agroecosystem services:
What is Soil Restoration?
Soil restoration involves improving the quality and productivity of soil that has been degraded due to various factors like erosion, pollution, or intensive agriculture practices. It aims to rebuild soil health, enhance biodiversity, and ensure the resilience of our agroecosystems.
Ideas For Soil Restoration:
1. Implementing Sustainable Agriculture Practices: By adopting agroecological practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry, we can help preserve soil health and minimize the use of chemical inputs.
2. Managing Soil Erosion: Contour plowing, terracing, and building windbreaks are effective methods to prevent soil erosion caused by wind and water. These practices help retain the topsoil and maintain its nutrient-rich composition.
3. Enhancing Soil Organic Matter: Adding organic materials such as compost or manure to the soil can significantly improve its fertility, water-holding capacity, and overall structure.
4. Promoting Biodiversity: Increasing plant diversity through mixed cropping or intercropping can have multiple benefits for soil health. Different crops have different nutrient requirements, which prevents nutrient depletion and improves overall soil nutrient content.
5. Implementing Conservation Tillage: Reducing or eliminating tillage helps minimize soil disturbance, prevents erosion, and improves water infiltration. No-till and reduced tillage systems are gaining popularity as sustainable alternatives to conventional tillage.
Recommendations For Soil Restoration:
1. Government Support: Governments should develop policies that promote sustainable soil management practices and provide financial incentives to farmers who adopt these practices.
2. Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of soil conservation and restoration among farmers, policymakers, and the general public is crucial for widespread adoption of sustainable soil management practices.
3. Research and Innovation: Investing in research and innovation is essential to develop new technologies and practices that improve soil restoration methods and enhance the resilience of agroecosystems.
4. Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration between scientists, farmers, and policymakers can facilitate knowledge sharing and the implementation of effective soil restoration strategies.
Listicle of Soil Restoration Techniques:
1. Crop Rotation: Rotating different crops within a field helps diversify the plant-microbe interactions, reduces pest and disease pressure, and improves soil fertility.
2. Composting: Composting organic waste materials like kitchen scraps, yard trimmings, and farm residues not only reduces waste but also enriches the soil with nutrients and beneficial microorganisms.
3. Biochar Application: Biochar, produced through the thermal decomposition of organic materials, can be added to the soil to improve its structure, nutrient retention, and microbial activity.
4. Alley Cropping: Planting trees or shrubs alongside annual crops in rows helps reduce erosion, provides shade, and enhances organic matter input to the soil.
5. Green Manure Cover Crops: Growing cover crops like legumes, grasses, or brassicas during fallow periods helps suppress weeds, fix nitrogen in the soil, and improve soil structure.
Question & Answer:
Q: How long does soil restoration take?
A: The time required for soil restoration varies depending on the degree of degradation and the techniques implemented. It can range from a few years to several decades.
Q: Can soil restoration prevent soil erosion?
A: Yes, adopting soil restoration practices like conservation tillage, contour plowing, and terracing can significantly reduce soil erosion rates.
Summary of Soil Restoration:
Soil restoration is crucial for ensuring long-term food security, preserving biodiversity, and mitigating climate change. By implementing sustainable practices, promoting biodiversity, and investing in research and innovation, we can restore soil functions and agroecosystem services. It's time to recognize the importance of soil and take action to protect this valuable resource for future generations.
I hope this post has shed some light on the importance of soil restoration. Remember, we all have a role to play in preserving our environment. Let's join hands and work towards a healthier and more sustainable future!
Post a Comment for "Agroecosystem Restoration For Biodiversity Conservation"