Agri-Food Waste Reduction And Upcycling Innovations
Recycling and valorization of agri-food waste have become essential in our efforts to create a more sustainable future. As we strive towards achieving a circular economy, finding innovative ways to repurpose waste from the agricultural and food sectors is crucial. By doing so, we can not only reduce the environmental impact of these industries but also unlock valuable resources that would otherwise go to waste.
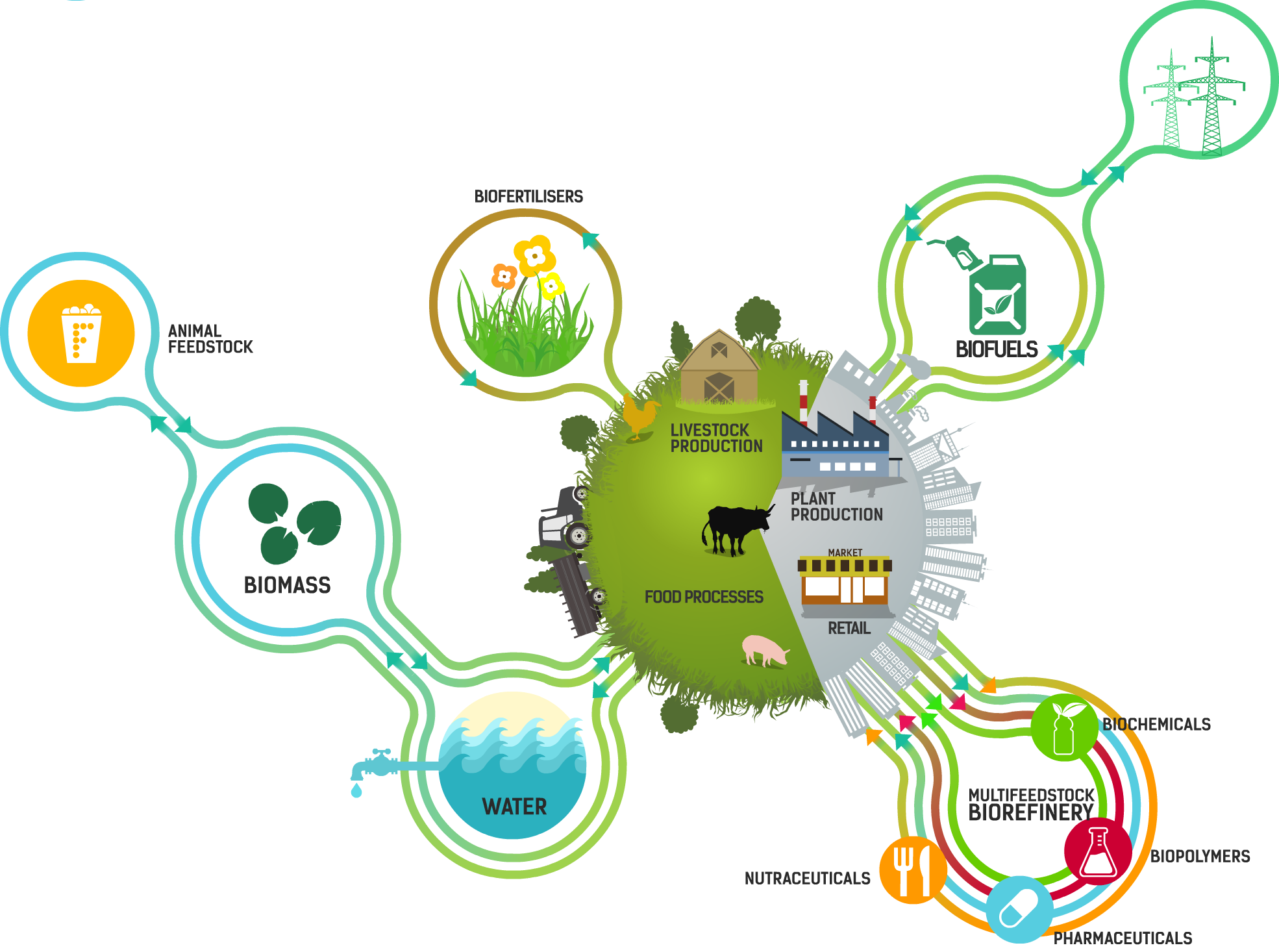
In this article, we will explore the importance of recycling and valorization of agri-food waste and delve into various strategies and solutions that can be implemented. Let us embark on this journey towards a more sustainable and efficient use of our resources.
What is Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization?
Agri-food waste recycling and valorization refer to the processes of repurposing and transforming waste generated from agricultural and food production activities into valuable products and resources. Traditional waste management practices, such as landfilling or incineration, are no longer viable options in the face of increasing waste generation and environmental concerns.
Recycling and valorization come in to tackle these challenges by redirecting waste from landfills and transforming it into usable materials, energy, or other valuable outputs. By doing so, we can minimize the negative impact of waste while also creating economic opportunities and reducing the consumption of virgin resources.
Ideas For Recycling and Valorization of Agri-Food Waste
There are numerous ideas and approaches that can be adopted to recycle and valorize agri-food waste. Let's explore some of the most promising ones:
- Biogas Production: One popular method involves the utilization of anaerobic digestion, a process where organic waste is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen, to produce biogas. Biogas can be subsequently used as a renewable energy source for heating, electricity generation, or as a vehicle fuel.
- Composting: Composting is a natural and environmentally friendly way to recycle organic waste, including agri-food waste. Through the decomposition of organic matter, compost is created, which can then be used as a nutrient-rich soil amendment for agriculture or landscaping purposes.
- Animal Feed Production: Certain types of agri-food waste, such as vegetable trimmings or by-products from food processing, can be repurposed as animal feed. This not only reduces waste but also provides a sustainable alternative to conventional feed sources.
- Food Waste Reduction: While not a recycling or valorization method per se, reducing food waste is an essential part of the overall strategy. By minimizing food waste at various stages of the supply chain, we can prevent unnecessary waste generation in the first place.
- Pharmaceutical or Nutraceutical Extraction: Agri-food waste often contains valuable compounds that can be extracted for use in pharmaceutical or nutraceutical products. This approach adds value to waste materials and promotes the concept of a circular economy.
Recommendations For Efficient Waste Management
Based on the ideas above, it is evident that efficient waste management is essential for the successful recycling and valorization of agri-food waste. Here are some recommendations to ensure the effectiveness of waste management practices:
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of recycling and valorization of agri-food waste is crucial. Education programs can help individuals and organizations understand the environmental and economic benefits of these practices, encouraging their adoption.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Building strong collaborations and partnerships between farmers, food producers, waste management agencies, and researchers is necessary. By working together, we can develop innovative solutions and share knowledge and resources for effective waste management.
- Policy Support: Governments can play a significant role in promoting efficient waste management through the implementation of supportive policies and regulations. These policies can incentivize recycling and valorization practices and provide a framework for sustainable waste management.
- Investment in Research and Development: Continuous research and development in waste management technologies, such as biogas production or composting techniques, are essential. Investing in these areas can lead to the discovery of new and more efficient methods of recycling and valorization.
- Integration of Circular Economy Principles: Adopting circular economy principles in agri-food waste management is crucial to maximize resource efficiency and minimize waste generation. This involves designing waste management systems that prioritize reuse, recycling, and the creation of value from waste.
Listicle of Successful Agri-Food Waste Recycling Projects
Several successful projects around the world showcase the potential of agri-food waste recycling and valorization. Here are some noteworthy examples:
- Project A: In country X, a company has developed an innovative biogas production system that utilizes agri-food waste from local farms and food processing facilities. The biogas is then used to power nearby communities, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Project B: A research institute in country Y has developed a novel technique to extract valuable compounds from agri-food waste, specifically targeting the nutraceutical industry. This project contributes to the creation of a circular economy by repurposing waste for beneficial applications.
- Project C: In country Z, a coalition of farmers, food producers, and waste management agencies has established a comprehensive composting network. The resulting compost is utilized by local farmers to enhance soil health and fertility, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers.
Question & Answer
Q: How does recycling and valorization of agri-food waste contribute to sustainability?
A: Recycling and valorization reduce the environmental impact of waste by minimizing its disposal in landfills or incineration. Additionally, these practices create economic opportunities, reduce resource consumption, and promote the principles of a circular economy.
Q: Can agri-food waste recycling and valorization be implemented on a small scale, such as in household settings?
A: Absolutely! Small-scale composting systems or biogas digesters can be implemented in households or community gardens to recycle organic waste. This not only reduces waste but also provides a sustainable source of compost or energy.
Q: Are there any challenges associated with the recycling and valorization of agri-food waste?
A: Yes, some challenges include the efficient collection and sorting of waste, technological limitations, and the need for proper infrastructure. However, with collaborative efforts and continuous research and development, these challenges can be overcome.
Summary
The recycling and valorization of agri-food waste are vital components of a sustainable future. By repurposing waste materials, we can reduce environmental pollution, create economic opportunities, and minimize resource consumption. Biogas production, composting, animal feed production, and the extraction of valuable compounds are among the many strategies employed in recycling and valorization. Efficient waste management practices, collaborations, policy support, and research are crucial for the success of these initiatives. Through these efforts, we can move towards a circular economy that prioritizes resource efficiency and waste reduction.
In conclusion, let us embrace the potential of recycling and valorization of agri-food waste and strive towards transformative change in our agricultural and food industries. Together, we can create a more sustainable future for generations to come.

Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Waste Reduction And Upcycling Innovations"