Smart Farm Management Systems For Increased Efficiency
Agriculture has come a long way in recent years, thanks to advancements in technology and the rise of smart farms. These innovative systems utilize cutting-edge technologies to optimize and streamline the farming process, increasing efficiency and productivity while minimizing environmental impact. However, it is crucial to question the sustainability of smart farms and their long-term implications.
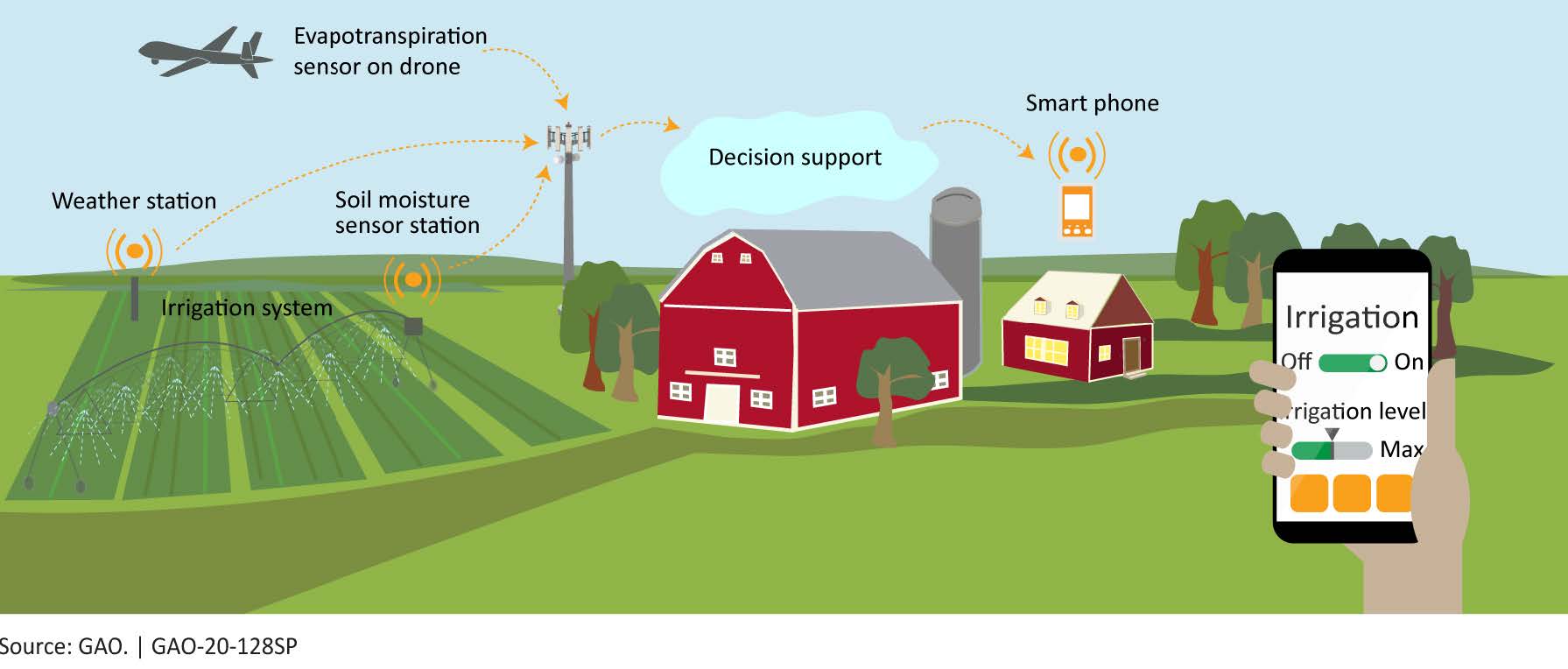
Smart farms, also known as precision agriculture systems, are a combination of various technologies and techniques that aid in the monitoring and management of agricultural practices. These systems incorporate sensors, drones, robotics, and data analytics to collect real-time information about soil conditions, weather patterns, crop health, and more.
One of the primary goals of smart farms is to optimize resource utilization, including water, fertilizer, and energy, to reduce waste and increase efficiency. By monitoring crop conditions and applying resources precisely where and when they are needed, farmers can minimize input costs and environmental impact while maximizing yields.
It is important to acknowledge that the sustainability of smart farms goes beyond their impact on the environment. A sustainable smart farm should also address social and economic aspects of agriculture, such as food security, farmer livelihoods, and rural development.
What is the Role of Technology in Smart Farms?
Technology plays a central role in the functioning of smart farms. The integration of sensors, drones, and robotics enables farmers to collect detailed data about their crops and make informed decisions based on real-time information. These technologies assist in:
- Monitoring soil conditions: Soil sensors help farmers assess various parameters like moisture levels, temperature, pH levels, and nutrient content. This data allows farmers to optimize irrigation and fertilizer application, reducing resource waste.
- Precision planting: Smart farms utilize GPS-guided machinery to ensure accurate and uniform planting of crops. This technology enables farmers to optimize seed placement, resulting in better germination and overall crop development.
- Crop monitoring: Drones equipped with multi-spectral imaging cameras capture detailed images of crops, enabling farmers to identify early signs of disease, nutrient deficiencies, or pest infestations. Real-time data from drones helps farmers intervene promptly and mitigate crop losses.
- Automation of tasks: Robotics and automation technologies are employed in various farming operations, such as harvesting, weeding, and application of pesticides. These technologies reduce labor-intensive tasks and improve efficiency.
Ideas For Improving Smart Farm Sustainability
While smart farms offer significant advantages in terms of efficiency and productivity, there is always room for improvement to enhance their sustainability. Here are a few ideas that can contribute to the sustainability of smart farms:
- Renewable energy integration: Smart farms can harness renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to power their operations. Investing in renewable energy not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also provides a reliable and sustainable energy source on-site.
- Water conservation techniques: Agriculture accounts for a substantial amount of global water consumption. Implementing water conservation techniques, such as drip irrigation and precision water application, can help minimize water wastage and promote sustainable water management.
- Data-driven decision-making: Smart farms generate vast amounts of data regarding crop conditions, weather patterns, and resource usage. Utilizing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms can optimize decision-making processes and resource allocation, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
- Crop diversification: Growing a diverse range of crops on smart farms can enhance soil health, reduce the risk of monocultures, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. Crop rotation and intercropping techniques can help maintain soil fertility, reduce pest outbreaks, and improve biodiversity.
Recommendations For a Sustainable Smart Farm
Building and maintaining a sustainable smart farm requires careful planning and implementation. Here are some recommendations to ensure the long-term sustainability of smart farms:
- Education and training: Farmers need access to comprehensive training programs to familiarize themselves with the latest technologies and best practices in smart farming. Promoting education and training can equip farmers with the necessary skills to make informed decisions and optimize resource usage.
- Collaboration and knowledge-sharing: Encouraging collaboration among farmers, researchers, and technology providers is essential for fostering innovation and driving sustainable practices in smart farming. Knowledge-sharing platforms, conferences, and workshops can facilitate the exchange of ideas and experiences.
- Policy support: Governments and policymakers play a vital role in promoting sustainable agriculture. Offering financial incentives, tax breaks, and subsidies for adopting smart farming technologies can encourage farmers to invest in sustainable practices.
- Data privacy and security: With the increasing use of data analytics and internet-connected technologies, data privacy and security become paramount. Establishing robust protocols and regulations to protect farmers' data and ensuring responsible data usage and management are crucial for the successful and sustainable implementation of smart farms.
A Listicle of Benefits Associated With Smart Farms
Smart farms offer numerous benefits, both for farmers and the environment. Here is a listicle highlighting the advantages of adopting smart farming practices:
- Increase in crop yields
- Reduction in resource wastage
- Optimized resource utilization
- Enhanced monitoring and early detection of crop diseases and pests
- Improved soil health and fertility
- Water conservation and sustainable water management
- Improved farm productivity and efficiency
- Reduction in chemical and pesticide use
- Optimized energy consumption
- Promotion of biodiversity and ecosystem health
Question & Answer Session
Q: Can smart farms be implemented on a small scale?
A: Yes, smart farms can be scaled to fit any size, from small-scale operations to large commercial farms. The technology can be adapted to suit the specific needs and resources available to farmers.
Q: Are smart farms cost-effective?
A: While the initial setup costs of smart farms may be higher, the long-term benefits, such as increased yields, improved resource utilization, and reduced wastage, often outweigh the investment. Smart farms can lead to significant cost savings in the long run.
Q: How can smart farms contribute to food security?
A: By optimizing resource utilization and increasing crop yields, smart farms have the potential to contribute to food security. These farms can help meet the growing demand for food while minimizing the environmental impact of agriculture.
Summing Up
Smart farms hold tremendous potential to revolutionize the agricultural industry, making it more sustainable, efficient, and productive. By incorporating advanced technologies and data analytics, farmers can optimize resource usage and reduce environmental impact. However, achieving true sustainability requires addressing social, economic, and environmental aspects of agriculture.
The ideas, recommendations, and benefits discussed in this article showcase the potential avenues for improving the sustainability of smart farms. It is essential for stakeholders, including farmers, researchers, and policymakers, to work together to ensure the responsible and effective implementation of smart farming practices.
Embracing smart farming not only benefits farmers but also the wider community by promoting food security, reducing environmental degradation, and fostering economic development. The future of agriculture lies in striking the right balance between technological advancements and sustainable practices.
Post a Comment for "Smart Farm Management Systems For Increased Efficiency"