Agri-Food Supply Chain Traceability And Quality Assurance
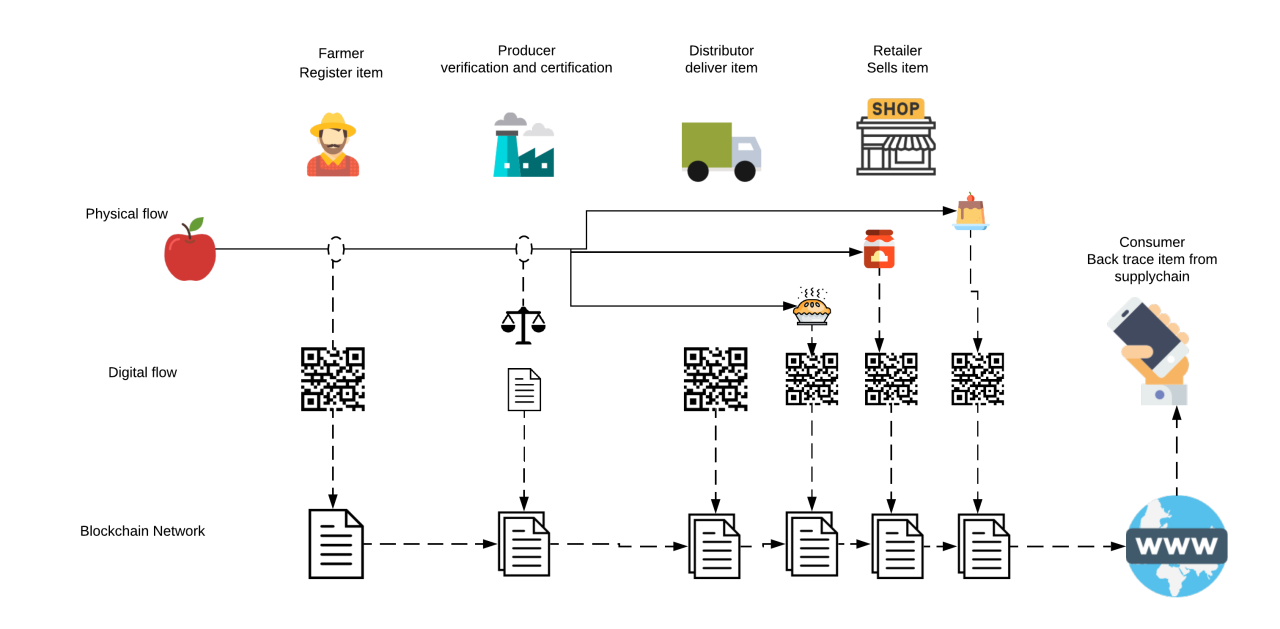
Traceability is an essential aspect of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana that requires careful management and monitoring. With the increasing global demand for food products, it is crucial to ensure the safety, quality, and authenticity of the products being consumed. However, the traditional methods of tracking and tracing the supply chain have proven to be inefficient and prone to errors. To address these challenges, blockchain technology has emerged as a promising solution.
Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and immutable ledger that allows for transparent and secure record-keeping. By leveraging this technology, Ghana's agri-food supply chain can achieve enhanced traceability, thereby improving food safety and reducing fraud and counterfeiting. This post explores the potential applications and benefits of using blockchain for traceability in the agri-food supply chain in Ghana.
What is Traceability in the Agri-food Supply Chain?
Traceability refers to the ability to track and trace the movement of products and their associated information throughout the supply chain. It involves capturing and recording data at various stages, including production, processing, packaging, and distribution. This data can include information about the origin of the product, its quality, certifications, and other relevant details.
The primary purpose of traceability is to ensure transparency, accountability, and trust in the supply chain. By providing a complete view of the product's journey from farm to fork, traceability enables consumers to make informed choices about the food they consume. It also helps in identifying and addressing issues related to food safety, quality control, and sustainability.
Ideas For Implementing Blockchain Traceability in Ghana's Agri-food Supply Chain
Implementing blockchain technology for traceability in Ghana's agri-food supply chain can revolutionize the industry and provide numerous benefits. Here are a few ideas for leveraging blockchain in this context:
- Secure Record-Keeping: Blockchain technology ensures secure record-keeping by providing an immutable ledger that cannot be tampered with. This feature can help in preventing fraud, counterfeiting, and other illegal activities that may occur in the supply chain.
- Enhanced Transparency: By leveraging blockchain, Ghana's agri-food supply chain can achieve greater transparency, allowing all stakeholders to access and verify information in real-time. This transparency builds trust among participants and enables consumers to make more informed decisions.
- Product Authentication: Blockchain can be utilized to authenticate and verify the authenticity of products. By recording key information, such as certifications and quality control measures, on the blockchain, consumers can trust that the products they are purchasing are genuine.
- Efficient Recall Management: In case of a product recall, blockchain technology can streamline the process by quickly identifying the affected products and their sources. This can save valuable time and resources, ensuring timely action to prevent further damage.
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: Blockchain can facilitate the automation of supply chain processes through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts can ensure timely payments, optimize inventory management, and eliminate intermediaries, resulting in improved efficiency and cost savings.
Recommendations for Blockchain Adoption in Ghana's Agri-food Supply Chain
While implementing blockchain technology in Ghana's agri-food supply chain holds significant promise, certain recommendations should be considered to ensure a successful adoption:
- Collaboration and Standardization: Collaboration among stakeholders, including farmers, producers, distributors, retailers, and regulatory bodies, is crucial for the successful implementation of blockchain traceability. Standardization of data formats, protocols, and interfaces is also essential to ensure interoperability.
- Capacity Building: Adequate training and capacity building programs should be conducted to educate stakeholders about blockchain technology and its implementation. This will help in overcoming any potential resistance or skepticism towards adopting this new technology.
- Infrastructure Development: To fully leverage blockchain technology, adequate infrastructure, such as internet connectivity and digital platforms, must be developed. This will enable seamless data exchange and ensure widespread adoption.
- Data Privacy and Security: As blockchain involves sharing sensitive data, robust measures must be in place to protect privacy and ensure data security. Implementing encryption mechanisms and access controls can help in mitigating risks associated with data breaches.
- Regulatory Framework: Clear and supportive regulatory frameworks should be developed to govern the use of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain. This will provide legal certainty and address any concerns regarding liability, intellectual property, and data ownership.
Listicle of Benefits of Blockchain Traceability in Ghana's Agri-food Supply Chain
1. Enhanced Food Safety: Blockchain traceability enables real-time monitoring and identification of potential risks, allowing for quick action to mitigate foodborne illnesses.
2. Fraud Prevention: The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate or counterfeit data, reducing the risk of fraud in the supply chain.
3. Supply Chain Efficiency: Automation through smart contracts eliminates the need for intermediaries, streamlining processes and reducing costs.
4. Consumer Trust: Transparent and verified information on the blockchain builds trust among consumers, resulting in increased brand loyalty.
5. Sustainable Agriculture: Blockchain can track and verify sustainability certifications, encouraging environmentally-friendly practices in the agri-food industry.
Question & Answer
Q: How does blockchain technology ensure the security of data in the agri-food supply chain?A: Blockchain technology ensures data security through its decentralized and immutable nature. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with, providing data integrity and eliminating the risk of unauthorized modifications. Q: How can blockchain traceability benefit farmers in Ghana?
A: Blockchain traceability can benefit farmers by providing them with a transparent and fair marketplace. By recording the origin and quality of their products on the blockchain, farmers can access a wider range of buyers, negotiate better prices, and build trust among consumers.
Summary of the Benefits of Blockchain Traceability in Ghana's Agri-food Supply Chain
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize traceability in Ghana's agri-food supply chain. By ensuring secure record-keeping, enhancing transparency, and enabling efficient recall management, blockchain can improve food safety, prevent fraud, and streamline supply chain processes. However, successful adoption requires collaboration, capacity building, infrastructure development, data privacy and security measures, and supportive regulatory frameworks. The benefits of blockchain traceability include enhanced food safety, fraud prevention, supply chain efficiency, consumer trust, and sustainable agriculture.

Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Supply Chain Traceability And Quality Assurance"