Agroecology Promoting Ecological Balance And Pest Management
Agroecology is an important topic in the field of agriculture and environmental science. It focuses on sustainable farming practices that help promote biodiversity, protect the environment, and improve the overall well-being of the farming communities. In this post, we will explore the various aspects of agroecology and its significance in today's world.
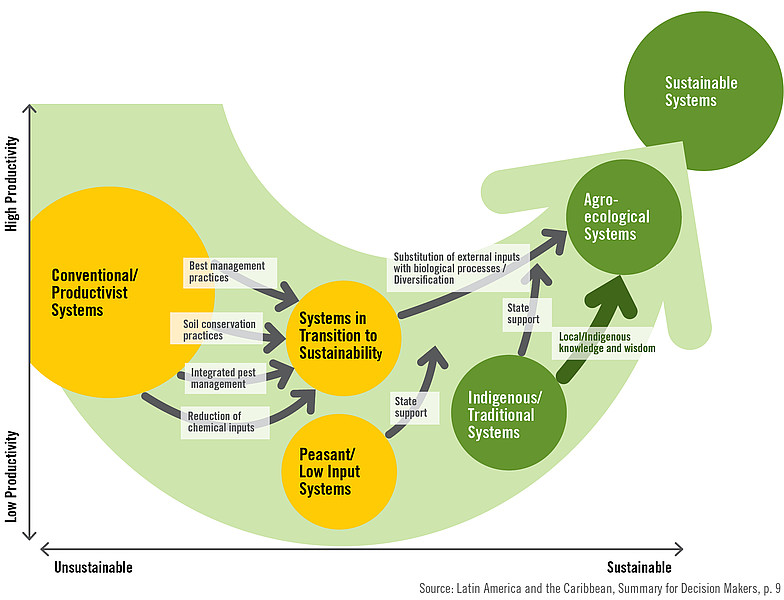
Agroecology is a holistic approach to agriculture that considers the ecological, economic, and social aspects of farming. It emphasizes the use of local resources, organic farming techniques, and the integration of crops and livestock. By adopting agroecological practices, farmers can reduce their dependence on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, conserve water, and enhance soil fertility.
One of the key principles of agroecology is promoting biodiversity on farms. By planting different types of crops and incorporating natural habitats, farmers can create a balanced ecosystem that supports beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. This helps in natural pest control and reduces the need for chemical pesticides.
Agroecology also promotes the use of organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, which improves soil health and fertility. Healthy soil is essential for plant growth and resilience, and it also helps in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change.
In addition to environmental benefits, agroecology has several social and economic advantages. By diversifying their crops, farmers can reduce the risk of crop failure and market fluctuations. This leads to increased food security and income stability for farming communities. Agroecological practices also promote local food systems and strengthen community ties.
What is the impact of agroecology on climate change?
Agroecology plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change. Unlike conventional farming, which heavily relies on synthetic inputs, agroecological practices focus on natural and sustainable solutions. By reducing chemical inputs, agroecology helps in minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the integration of trees and other perennial crops in agroecosystems helps in carbon sequestration, contributing to the reduction of atmospheric CO2 levels.
Moreover, agroecological techniques, such as conservation agriculture and agroforestry, promote soil health and resilience. Healthy soils have a higher capacity to retain water, reducing the risk of droughts and floods, which are becoming increasingly common due to climate change.
Ideas for implementing agroecology in farming practices
1. Crop rotation: Instead of growing the same crop year after year, farmers can implement crop rotation techniques to break pest cycles and improve soil fertility.
2. Intercropping: Planting different crops together can promote biodiversity and enhance soil health. For example, growing legumes alongside cereals helps in nitrogen fixation and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
3. Agroforestry: Integrating trees with crops and livestock can provide additional income sources, improve soil structure, and enhance biodiversity on farms.
4. Organic fertilizers: Using organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, instead of synthetic chemicals, helps in building soil fertility and reducing environmental pollution.
5. Conservation agriculture: Practices like minimal tillage, soil cover, and crop residue management help in soil conservation and water retention.
Recommendations for policymakers and agricultural institutions
1. Support research and education: Governments and agricultural institutions should invest in research and education to promote agroecological practices. This includes developing improved crop varieties, studying the impact of agroecology on biodiversity, and providing training to farmers.
2. Financial incentives: Policymakers can provide financial support to farmers who adopt agroecological practices. This can be in the form of subsidies, grants, or tax incentives.
3. Policy reforms: Governments should develop policies that encourage sustainable farming practices and discourage the use of harmful chemicals and monoculture farming methods.
4. Collaborations and knowledge sharing: Agricultural institutions should promote collaborations between researchers, farmers, and policymakers to exchange knowledge and best practices in agroecology.
Listicle of benefits of agroecology
- Enhanced biodiversity: Agroecology promotes the conservation of native flora and fauna by creating diverse ecosystems on farms.
- Improved soil health: By relying on organic fertilizers and practicing soil conservation techniques, agroecology helps in building healthy and fertile soils.
- Reduced chemical inputs: Agroecological practices lower the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, reducing environmental pollution and health risks.
- Resilience to climate change: Agroecosystems built on the principles of agroecology are more resilient to extreme weather conditions, such as droughts and floods.
- Food security: Diversifying crops and promoting local food systems improves food security, ensuring a stable supply of nutritious food for communities.
- Sustainable livelihoods: Agroecology provides income stability for farmers by reducing market risks and dependence on external inputs.
- Water conservation: Agroecological practices, such as minimal tillage and soil cover, help in retaining water in the soil, reducing water runoff and enhancing water availability.
- Carbon sequestration: The integration of trees and perennial crops in agroecosystems helps in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change.
- Community empowerment: Agroecology promotes local food systems, strengthens community ties, and empowers farmers.
- Improved human health: By reducing the use of synthetic chemicals, agroecological practices contribute to improved human health and well-being.
Question & Answer
1. Q: Is agroecology only applicable to small-scale farming?
A: No, agroecology can be implemented in both small-scale and large-scale farming systems. The key principles of agroecology, such as biodiversity promotion and sustainable practices, can be adapted to various farming contexts.
2. Q: How does agroecology contribute to sustainable development?
A: Agroecology promotes environmentally friendly farming practices that conserve natural resources, support local communities, and ensure long-term food security. By addressing social, economic, and ecological aspects, agroecology contributes to a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.
3. Q: What are the challenges in adopting agroecological practices?
A: Some of the challenges in adopting agroecological practices include limited access to knowledge and training, resistance to change, and initial investment costs. However, with the right support from policymakers and agricultural institutions, these challenges can be overcome.
Summary of agroecology and its significance
Agroecology is a holistic approach to agriculture that emphasizes sustainable practices, biodiversity promotion, and community empowerment. It offers numerous benefits, including enhanced soil health, reduced chemical inputs, resilience to climate change, and improved food security. By adopting agroecological practices, farmers can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system that supports environmental conservation and the well-being of farming communities.
Disclaimer: The above content is based on the information obtained from trusted sources, but the exact source of the data is unknown.

Post a Comment for "Agroecology Promoting Ecological Balance And Pest Management"