Sustainable Livestock Grazing Rotational Systems And Landscape Management
Rotational livestock grazing is a practice that has been gaining recognition for its numerous benefits. Not only does it contribute to climate change mitigation, but it also has significant economic advantages. In this post, we will explore the positive impacts of rotational grazing and discuss ideas, recommendations, and answer common questions relating to this sustainable farming technique.
But before we delve into the details, let's understand what rotational livestock grazing actually means. This practice involves dividing a pasture into smaller sections, known as paddocks, and moving the livestock from one paddock to another at regular intervals. By allowing the animals to graze on a specific paddock for a limited time and then rotating them, farmers can mimic the natural movement patterns of wild herds. This approach offers a range of benefits for both the animals and the environment.
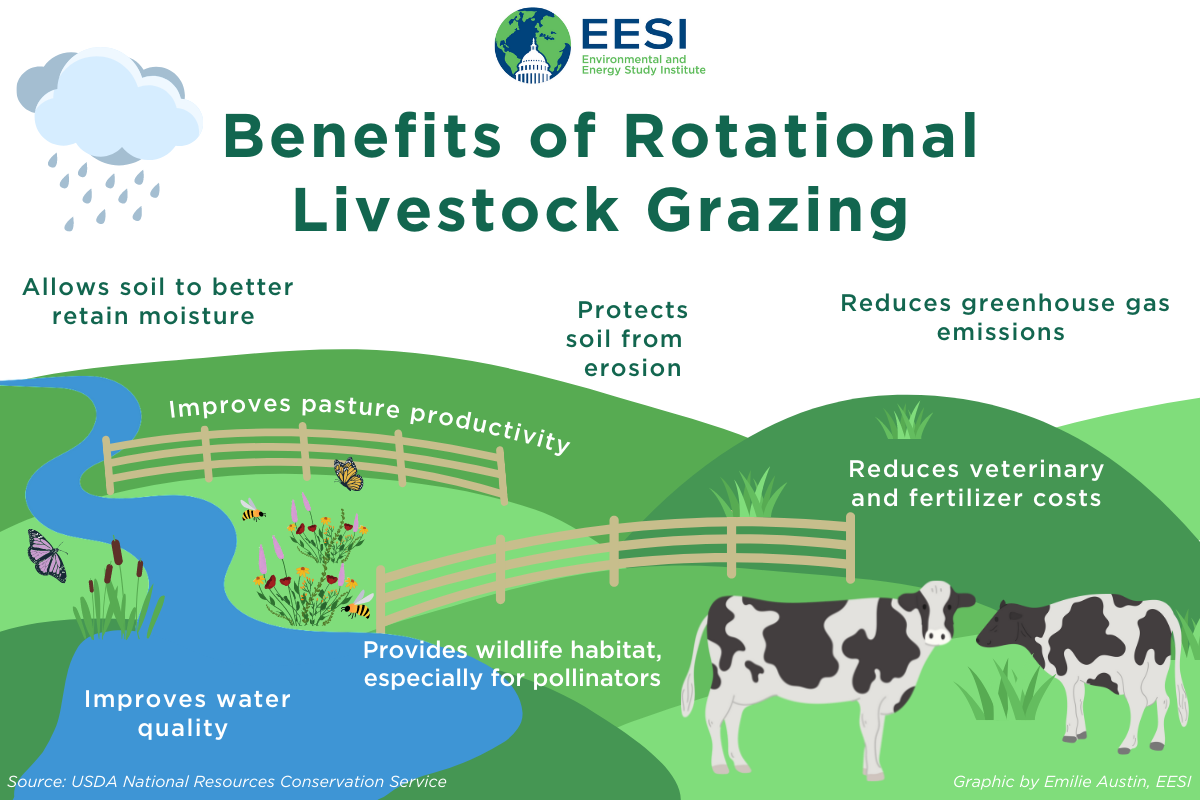
Rotational grazing helps combat climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil. When livestock continuously graze on a single pasture, they tend to overgraze, which leads to the degradation of plants and reduces the soil's ability to store carbon. However, with rotational grazing, the livestock can only graze a specific area for a short time, allowing the grass to recover and absorb more carbon from the atmosphere.
Additionally, rotational grazing improves soil health and fertility. The movement of livestock stimulates the soil, and their waste acts as a natural fertilizer. This results in healthier vegetation and an increased capacity for water retention in the soil, reducing the risk of erosion and enhancing the overall sustainability of the land.
From an economic perspective, rotational grazing can significantly benefit farmers. By implementing this practice, farmers can reduce the need for purchased inputs, such as chemical fertilizers and feed. The movement of livestock also eliminates the need for expensive machinery to distribute manure, as the animals naturally distribute it across the paddocks. Consequently, farmers can experience reduced costs and increased profitability.
What is Rotational Grazing?
As mentioned earlier, rotational grazing involves dividing a pasture into smaller sections called paddocks and moving livestock from one paddock to another at regular intervals. This system promotes sustainable and efficient land management while providing optimal nutrition for the animals.
The key principle of rotational grazing is to allow livestock to graze on a single paddock for a specific time, typically a few days, and then rotate them to a new paddock. This rest period allows the grass in the previously grazed paddock to regrow, ensuring a continual source of fresh and nutritious forage.
The duration of each grazing period and the length of rest time between rotations depend on various factors, including the size of the paddocks, number of livestock, and the availability of forage. Farmers need to carefully plan and manage the rotation schedule to achieve the best results for both the animals and the environment.
Ideas For Implementing Rotational Grazing
If you are a farmer interested in implementing rotational grazing on your land, here are some useful ideas to consider:
- Start with a small-scale trial: Begin by implementing rotational grazing in a smaller area to understand its dynamics and assess the impact on your farming operation. This will help you refine your approach before scaling up.
- Develop a paddock layout plan: Divide your pasture into paddocks of equal size or allocate larger areas for livestock with higher nutritional requirements. Proper fencing is crucial to ensure effective rotation.
- Consider grazing intensity and stocking rates: Monitor the livestock's grazing patterns and adjust the number of animals per paddock accordingly. Avoid overgrazing to maintain healthy vegetation.
- Pay attention to forage selection: Encourage the consumption of diverse plant species by rotating livestock through different paddocks. This promotes biodiversity and improves the nutritional content of the animal's diet.
- Manage water sources efficiently: Ensure that all paddocks have access to clean water sources. Consider implementing gravity-fed watering systems or using portable water troughs for easy movement between paddocks.
Recommendations for Successful Rotational Grazing
Based on experience and research, here are some recommendations to ensure successful implementation of rotational grazing:
- Maintain a flexible rotation schedule: Adapt your rotation schedule based on the weather, season, and forage availability. Consider adjusting the duration of grazing and rest periods to optimize the health of the pasture.
- Monitor forage growth: Regularly assess the growth of the forage in each paddock to determine the appropriate time for livestock to graze. Adjust the rotation schedule accordingly to maximize forage production.
- Implement rotational grazing by animal class: If you have multiple livestock species or groups with varying nutritional needs, divide your pasture into separate systems to provide tailored grazing conditions.
- Collaborate with other farmers: Participating in a cooperative grazing system allows for larger-scale rotational grazing, increased herd size, and shared knowledge and equipment resources.
- Seek guidance from experts: Consult agricultural extension services, local conservation organizations, or experienced farmers for guidance on rotational grazing practices specific to your region and livestock.
Listicle of Rotational Grazing Benefits
Rotational grazing offers a multitude of benefits for both the environment and farmers. Let's explore some of the advantages:
- Improved soil health and fertility
- Increased carbon sequestration
- Enhanced pasture productivity
- Reduced reliance on chemical inputs
- Lower feed costs
- Increased profitability
- Better water infiltration and retention
- Controlled weed growth
- Promotion of biodiversity
- Reduced soil erosion
Question & Answer about Rotational Grazing
Q: How often should livestock be rotated?
A: The frequency of rotation depends on factors such as livestock type, pasture condition, and forage availability. It is generally recommended to rotate the animals every few days to allow for optimal pasture regrowth.
Q: Can rotational grazing be implemented on hilly terrain?
A: Yes, rotational grazing can be adapted to hilly or sloping landscapes. Proper paddock layout and fencing can help ensure effective grazing management while preventing erosion.
Q: Does rotational grazing require additional labor?
A: Initially, rotational grazing may require some additional labor for fence maintenance and paddock setup. However, as the system becomes established, the workload often decreases, allowing farmers to efficiently manage their livestock.
Summary
Rotational livestock grazing is a sustainable farming practice that provides numerous environmental and economic benefits. By dividing pastures into smaller paddocks and regularly moving livestock between them, farmers can help combat climate change, enhance soil health, and reduce costs. Implementing rotational grazing requires careful planning, paddock layout design, and proper management. Farmers can seek advice from experts, collaborate with other farmers, and gradually scale up their operation for optimal results. With its potential to improve agricultural systems and contribute to a healthier planet, rotational grazing deserves greater attention and adoption in the farming community.
Post a Comment for "Sustainable Livestock Grazing Rotational Systems And Landscape Management"