Agri-Food Traceability Ensuring Transparency And Quality
Traceability of Agri-food Supply Chain in Ghana using blockchain
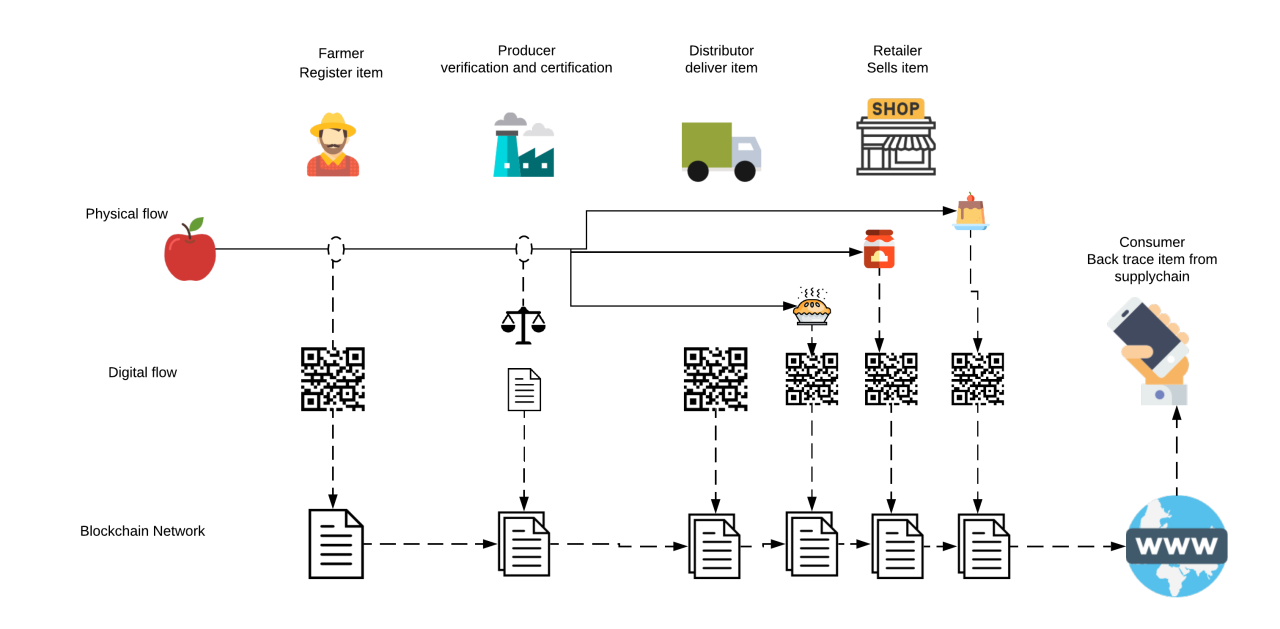
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize various industries, and one such industry is the agri-food supply chain. Ghana, with its booming agricultural sector, can greatly benefit from the implementation of blockchain-based systems to enhance traceability.
In recent years, there has been a growing demand for greater transparency and accountability in the food supply chain. Consumers want to know where their food comes from, how it is produced, and whether it meets quality standards and ethical practices. This demand has fueled the need for robust traceability systems that can provide accurate and real-time information about the journey of food from farm to fork.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable nature, offers a promising solution to address the challenges faced by the agri-food supply chain. By leveraging blockchain, Ghana can establish an efficient and transparent traceability system that builds trust among consumers while promoting fair trade practices and sustainable agriculture.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that enables the secure and transparent recording of transactions. It operates on a network of computers, known as nodes, which work together to verify and validate each transaction. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes permanent and cannot be altered or deleted.
Blockchain technology utilizes cryptographic algorithms to ensure the integrity and security of data. Each transaction is bundled into a block, which is connected to the previous block through a unique cryptographic hash. This creates a chain of blocks, hence the name blockchain.
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralization. Unlike traditional centralized systems, blockchain does not rely on a single authority or intermediary to validate and record transactions. Instead, it operates on a peer-to-peer network, where every participant has a copy of the blockchain.
Ideas For Implementing Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain in Ghana
The implementation of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain in Ghana can bring numerous benefits. Here are some ideas for leveraging blockchain technology:
- Enhanced Traceability: Blockchain can offer an immutable and auditable record of every transaction and movement within the supply chain. This can help in tracing the origin and journey of agri-food products, providing detailed information about their production, processing, and distribution.
- Ensuring Product Authenticity: Blockchain can be used to verify the authenticity of agricultural products, mitigating the risk of counterfeits and ensuring that consumers receive genuine and high-quality products.
- Promoting Fair Trade Practices: With blockchain, the agri-food supply chain can be more transparent, allowing consumers to make informed choices based on ethical and fair trade practices. Blockchain can facilitate the certification and validation of sustainability and fair trade standards.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can streamline supply chain operations by automating manual processes, reducing paperwork, and minimizing errors. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, can automate tasks such as payment settlements, quality checks, and compliance verification, leading to improved efficiency.
- Real-time Monitoring and Quality Control: Blockchain can enable real-time monitoring of agri-food products, ensuring their quality and safety throughout the entire supply chain. By integrating blockchain with IoT (Internet of Things) devices, data such as temperature, humidity, and location can be recorded on the blockchain, allowing stakeholders to track and monitor product conditions.
Recommendations For Implementing a Blockchain-based Traceability System
Implementing a blockchain-based traceability system in the agri-food supply chain requires careful planning and collaboration among various stakeholders. Here are some recommendations for a successful implementation:
- Collaboration: Establish partnerships and collaborations among farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and other relevant stakeholders to ensure the participation and commitment of all parties in implementing the traceability system.
- Standardization: Develop standardized protocols and data formats that can be used by all participants in the supply chain. This will ensure interoperability and seamless integration of data across different stages of the supply chain.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Provide the necessary infrastructure, such as reliable internet connectivity and robust hardware systems, to support the implementation of blockchain technology.
- Training and Education: Conduct training and awareness programs to educate stakeholders about the benefits and usage of blockchain technology. This will help in building trust and adoption of the system.
- Regulatory Framework: Establish a regulatory framework that governs the implementation of blockchain technology in the agri-food supply chain. This framework should address privacy, data protection, and legal considerations.
Listicle of Advantages of Implementing Blockchain in the Agri-food Supply Chain
- Improved transparency and trust among consumers
- Reduction in food fraud and counterfeiting
- Efficient supply chain operations
- Elimination of manual paperwork
- Enhanced food safety and quality control
- Verification of product authenticity
- Promotion of fair trade practices
- Real-time monitoring of agri-food products
- Cost savings through automation
- Facilitation of sustainability and ethical certifications
Question & Answer Session on Blockchain-based Traceability in the Agri-food Supply Chain
Q: How does blockchain ensure the authenticity of agricultural products?
A: Blockchain provides an immutable and transparent record of every transaction and movement within the supply chain. Each transaction is verified and recorded by multiple participants on the network, making it difficult to manipulate or counterfeit product information.
Q: Can blockchain improve food safety in the agri-food supply chain?
A: Yes, by integrating blockchain with IoT devices, stakeholders can monitor and record data such as temperature, humidity, and location in real-time. This enables quick identification of potential hazards and ensures that food safety standards are met throughout the supply chain.
Q: How can blockchain promote fair trade practices?
A: Blockchain enables the certification and validation of sustainability and fair trade standards. By recording the entire journey of agricultural products on the blockchain, consumers can make informed choices based on the transparency and ethical practices demonstrated by the supply chain participants.
Summary of Blockchain-based Traceability in the Agri-food Supply Chain in Ghana
Implementing blockchain technology in the agri-food supply chain in Ghana can bring numerous benefits such as enhanced traceability, improved transparency, and efficient supply chain management. By leveraging blockchain, Ghana can establish a robust traceability system that meets the growing demand for transparency and accountability in the food industry.
The successful implementation of a blockchain-based traceability system requires collaboration among stakeholders, standardization of protocols, investment in infrastructure, training and education, and the establishment of a regulatory framework. By addressing these aspects, Ghana can unlock the potential of blockchain and revolutionize its agri-food supply chain.

Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Traceability Ensuring Transparency And Quality"