Agri-Food Traceability Ensuring Transparency And Traceability
Traceability of Agri-food Supply Chain in Ghana using blockchain
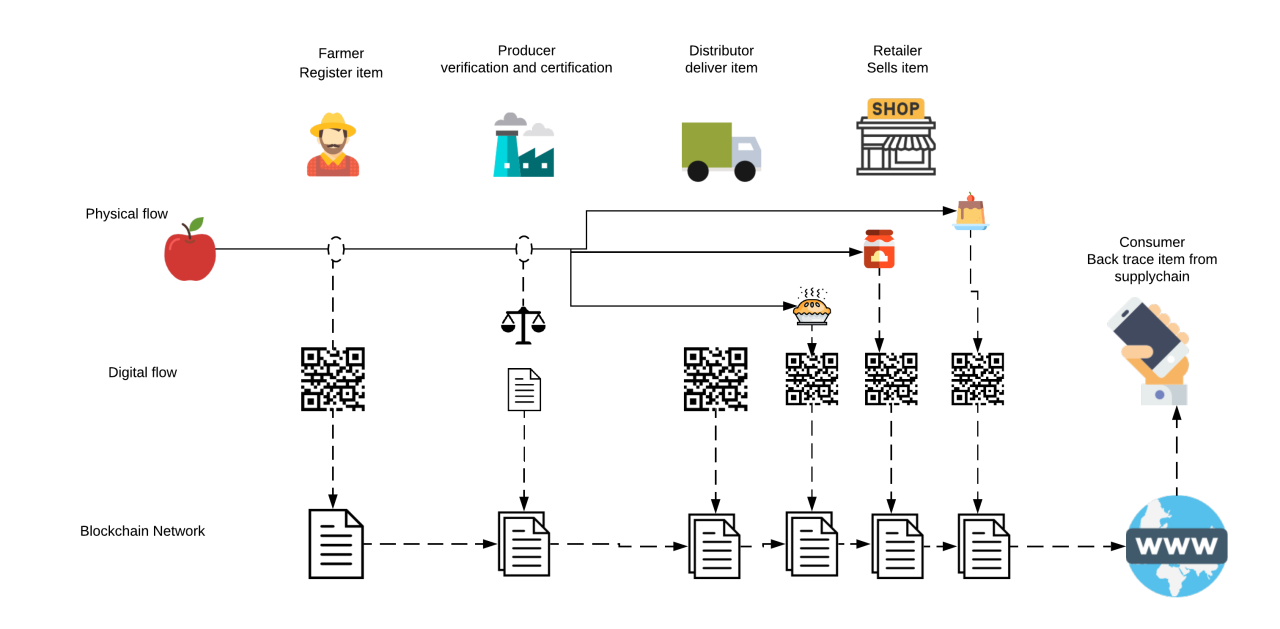
The agri-food supply chain plays a critical role in ensuring a steady and sustainable food supply for the population. However, ensuring transparency and traceability within this complex supply chain can be a challenging task due to various factors such as limited technology adoption and information asymmetry. Fortunately, the emergence of blockchain technology offers promising solutions to address these challenges.
Blockchain, often associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It provides a secure and transparent platform for data sharing and collaboration, making it ideal for enhancing traceability in the agri-food supply chain. Let's explore how blockchain can revolutionize the traceability of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana.
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized system that allows multiple parties to maintain and verify a shared digital ledger. It is composed of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a batch of transactions. The transactions are verified by consensus among the participants and added to the chain in a chronological order. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes permanent and tamper-proof, providing a high level of data integrity.
Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain does not rely on a single entity to control and validate the transactions. Instead, it operates on a peer-to-peer network, where each participant has a copy of the entire blockchain. This distributed nature of blockchain ensures that no single entity can manipulate the data, which enhances the security and trustworthiness of the system.
Ideas for Implementing Blockchain in Agri-food Supply Chain
Implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain can offer several benefits, ranging from increased transparency to improved efficiency. Let's explore some ideas for leveraging blockchain technology in Ghana's agri-food sector:
- Enhanced Traceability: By recording each step of the supply chain on the blockchain, stakeholders can track the origin and journey of agricultural products. This visibility ensures transparency and allows consumers to make informed choices about the food they consume.
- Reduced Counterfeit Products: Counterfeit products are a significant challenge in the agri-food industry, leading to losses for both consumers and producers. With blockchain, each product can be assigned a unique identifier that is recorded on the ledger. This prevents counterfeit products from entering the supply chain and protects both consumers and producers.
- Efficient Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can streamline supply chain processes by automating tasks and eliminating paperwork. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, can automatically execute predefined actions based on predefined conditions. This automation reduces administrative burdens and enhances efficiency in the agri-food supply chain.
- Improved Quality Control: Blockchain can facilitate real-time monitoring of product quality throughout the supply chain. IoT devices can be integrated with the blockchain, allowing information such as temperature and humidity to be recorded and verified. This enables timely interventions to maintain product quality and reduces the risk of spoiled or contaminated goods reaching consumers.
- Enhanced Farmer Payments: In many agri-food supply chains, farmers are often underpaid due to lack of transparency and information asymmetry. Blockchain can enable transparent and automated payment systems, ensuring that farmers receive fair compensation for their produce.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Blockchain can incentivize sustainable practices by recording and verifying certifications, such as organic or fair trade, on the ledger. This allows consumers to make eco-friendly choices and rewards farmers for adopting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Improved Food Safety: Blockchain can help identify and address food safety issues by providing real-time visibility into the entire supply chain. In case of a contamination outbreak or quality concern, the affected products can be quickly traced back to their source, enabling timely recalls and preventing further harm.
- Marketplace Integration: Blockchain can facilitate seamless integration between various marketplaces within the agri-food supply chain. It enables secure and transparent transactions between buyers and sellers, eliminating middlemen and reducing transaction costs.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: Blockchain provides a platform for secure and efficient data sharing among supply chain stakeholders. This fosters collaboration, information sharing, and collectively finding solutions to challenges faced by the agri-food industry.
- Consumer Engagement: By providing consumers with access to transparent and reliable information about the food they consume, blockchain can empower them to make informed choices. Consumers can verify the origin, production methods, and certifications of the products they purchase, thus promoting trust and sustainability in the agri-food sector.
Recommendations for Implementing Blockchain in Ghana's Agri-food Supply Chain
While the potential benefits of implementing blockchain in Ghana's agri-food supply chain are evident, several considerations need to be taken into account to ensure successful implementation. Here are some recommendations for effectively leveraging blockchain technology:
- Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Successful implementation requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, regulators, and technology providers. Engaging all relevant parties throughout the implementation process fosters a sense of ownership and ensures that the solution meets the specific needs of Ghana's agri-food industry.
- Infrastructure Development: Adequate infrastructure, such as reliable internet connectivity and data storage capabilities, is crucial for blockchain implementation. Investments in infrastructure development should be prioritized to enable seamless communication and data sharing across the supply chain.
- Data Standardization: Standardizing data formats and quality is essential to ensure interoperability and seamless integration of blockchain across different stages of the supply chain. Establishing common protocols and guidelines for data collection, storage, and sharing can facilitate smooth implementation and maximize the benefits of blockchain technology.
- Education and Awareness: Blockchain is still a relatively new technology, and awareness among stakeholders may be limited. Providing comprehensive training and educational programs can empower stakeholders to understand the potential of blockchain and encourage its adoption in the agri-food supply chain.
- Regulatory Framework: Developing a clear regulatory framework is crucial to ensure legal compliance and protect the interests of all stakeholders. Regulations should address issues such as data privacy, intellectual property rights, and dispute resolution, while also fostering innovation and growth in the agri-food sector.
- Scalability and Interoperability: As the agri-food supply chain involves multiple stakeholders and processes, scalability and interoperability of blockchain solutions are paramount. Implementing blockchain systems that can handle a large volume of transactions and seamlessly integrate with existing technologies will maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain.
- Pilot Projects and Proof of Concepts: Conducting pilot projects and proof of concepts can provide valuable insights into the feasibility and potential challenges of implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain. These small-scale initiatives allow stakeholders to test the technology in a controlled environment before scaling up the implementation.
- Long-term Sustainability: Establishing mechanisms for long-term sustainability is essential to ensure the continuous operation and evolution of the blockchain solution. This includes regular maintenance, upgrading of infrastructure, and adapting to changing technology and industry trends.
Listicle of Benefits of Blockchain in Agri-food Supply Chain
Blockchain technology offers numerous benefits for the agri-food supply chain in Ghana. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
- Transparency: Blockchain provides an immutable and transparent record of transactions, ensuring accountability and trust among stakeholders.
- Traceability: Each step of the supply chain can be recorded on the blockchain, enabling easy tracing of products' origin and journey.
- Security: Blockchain's decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms make it highly secure against data tampering and fraud.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts and automation reduce administrative burdens, streamline processes, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
- Quality Control: Real-time monitoring and IoT integration enable proactive measures to maintain product quality and prevent spoilage.
- Marketplace Integration: Blockchain facilitates secure and efficient transactions between buyers and sellers, eliminating intermediaries and reducing costs.
- Sustainability: Blockchain incentivizes sustainable practices by verifying and rewarding eco-friendly certifications.
- Consumer Trust: Transparent information empowers consumers to make informed choices and promotes trust in the food they consume.
- Reduced Counterfeit Products: Blockchain's unique identifiers prevent counterfeit products from entering the supply chain, protecting consumers and producers.
- Fair Compensation: Transparent payment systems ensure that farmers receive fair compensation for their produce, reducing income disparities.
Question & Answer
Q: How does blockchain ensure the authenticity of the data recorded on the ledger?
A: Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure and verify the data recorded on the ledger. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous transaction in the chain, creating a tamper-proof record of events. As the ledger is distributed among multiple participants, no single entity can manipulate the data without consensus from others.
Q: Can blockchain be applied to different commodities within the agri-food supply chain?
A: Yes, blockchain can be applied to various commodities within the agri-food supply chain, including crops, livestock, and processed food products. By recording each step of the supply chain, blockchain ensures transparency and traceability regardless of the commodity.
Q: How can blockchain contribute to reducing food waste in the agri-food supply chain?
A: Blockchain's real-time monitoring capabilities help identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the supply chain, enabling timely interventions. By preventing spoilage and facilitating efficient distribution, blockchain can reduce food waste and ensure a more sustainable agri-food system.
Summary of the Benefits of Blockchain in Agri-food Supply Chain
Blockchain technology holds immense potential for transforming the agri-food supply chain in Ghana. By ensuring transparency, traceability, and security, blockchain can address the challenges associated with limited technology adoption and information asymmetry. The implementation of blockchain in the agri-food sector can lead to numerous benefits, including enhanced traceability, reduced counterfeit products, improved quality control, and sustainable agriculture.
To harness the benefits of blockchain, it is important to consider factors such as collaboration among stakeholders, infrastructure development, data standardization, and regulatory frameworks. Pilot projects and proof of concepts can provide valuable insights, and continuous maintenance and upgrades are crucial for the long-term sustainability of blockchain solutions in the agri-food supply chain.
With the right approach and careful implementation, blockchain can revolutionize the agri-food supply chain in Ghana, fostering trust, transparency, and sustainability for all stakeholders involved.

Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Traceability Ensuring Transparency And Traceability"