Agri-Food Waste Management From Reduction To Resource Recovery
Recycling and valorization of agri-food waste is a crucial topic in today's world. With concerns over global food security and sustainability on the rise, finding innovative solutions to minimize waste and maximize resource utilization has become more important than ever.
In this article, we will explore the various aspects of agri-food waste recycling and valorization, discussing its significance, ideas for implementation, recommendations, and answering common questions surrounding this topic.
But first, let's take a moment to understand what agri-food waste recycling and valorization actually mean.
What is Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization?
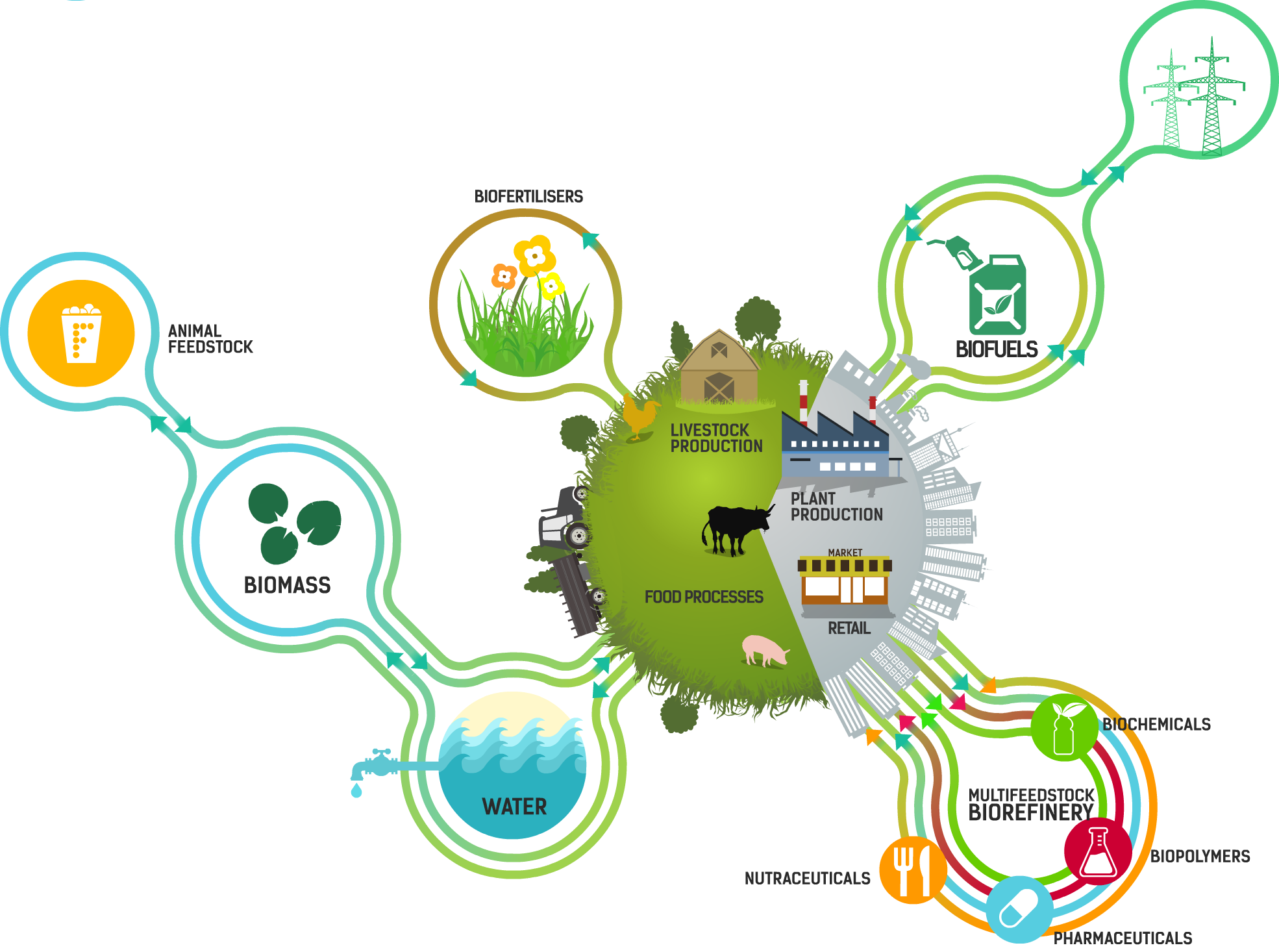
Agri-food waste recycling refers to the process of transforming waste materials generated during agricultural and food production activities into valuable products or resources. The objective is to minimize wastage, reduce environmental impact, and create a more sustainable food system.
Valorization, on the other hand, involves extracting maximum value from the waste by utilizing it in various ways. This can involve the production of biofuels, organic fertilizers, animal feed, or even using waste to generate energy.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the concept, let's delve into some ideas for implementing agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices.
Ideas For Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization
1. Composting: One of the simplest and most effective ways to recycle agri-food waste is through composting. By collecting organic waste materials such as fruit and vegetable peels, leftover food, and crop residues, and allowing them to decompose naturally, nutrient-rich compost can be produced. This compost can then be used as a natural fertilizer for plants.
2. Anaerobic Digestion: Anaerobic digestion is a process that involves breaking down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, resulting in the production of biogas and nutrient-rich digestate. The biogas can be used as a renewable energy source, while the digestate can be used as a fertilizer.
3. Biomass Conversion: Agri-food waste can be converted into biomass fuel pellets, which can be used for heating or electricity generation. Utilizing waste as a renewable energy source reduces dependence on fossil fuels and contributes to a greener and more sustainable energy sector.
4. Food Redistribution: Instead of throwing away surplus food, efforts should be made to redistribute it to those in need. Food banks, charitable organizations, and innovative technology-driven platforms can facilitate the redistribution process, ensuring that excess food is not wasted.
5. Animal Feed: Certain types of agri-food waste, such as wheat bran, corn stalks, and potato peels, can be transformed into animal feed. This reduces the need for dedicated feed crops and helps in the efficient utilization of waste materials.
6. Bioplastics: Agri-food waste, particularly plant-based materials, can be used to produce bioplastics. Bioplastics are a more sustainable alternative to traditional plastics, as they are biodegradable and have a lower carbon footprint.
7. Nutraceuticals: Agri-food waste contains valuable nutrients and bioactive compounds that can be extracted and used in the production of nutraceuticals. Nutraceuticals are products derived from food sources with proven health benefits, contributing to both human well-being and waste reduction.
8. Water Treatment: Some agri-food waste, such as grape pomace or coffee grounds, can be used in wastewater treatment processes. These waste materials have natural properties that aid in the removal of pollutants, making them a sustainable solution for water treatment.
9. Packaging Materials: Agri-food waste can be utilized in the production of eco-friendly packaging materials. By transforming waste into biodegradable packaging options, the reliance on non-recyclable and environmentally harmful packaging materials can be reduced.
10. Industrial Applications: Agri-food waste can also find applications in various industrial processes. For example, olive pits can be used as a fuel source in cement kilns, reducing the need for coal combustion and minimizing carbon emissions.
Now that we have explored several ideas for agri-food waste recycling and valorization, let's discuss some recommendations for implementing these practices effectively.
Recommendations For Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization
1. Collaboration: Collaboration between different stakeholders, including farmers, food processors, waste management companies, and policymakers, is crucial for the successful implementation of agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices. This collaboration ensures a holistic approach is taken, considering the entire supply chain.
2. Education and Awareness: Increasing awareness and educating the public about the importance of agri-food waste recycling and valorization is essential. By understanding the impact of individual actions and choices, consumers can actively participate in waste reduction initiatives and support sustainable practices.
3. Incentives: Providing incentives for individuals and businesses to adopt agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices can be highly motivating. These incentives can be in the form of tax credits, grants, or other financial benefits that encourage the implementation of sustainable waste management practices.
4. Regulatory Frameworks: Governments can play a pivotal role in promoting agri-food waste recycling and valorization by establishing regulatory frameworks and standards. By setting clear guidelines for waste management practices, authorities can create an enabling environment that promotes sustainable solutions.
5. Technological Innovation: Investing in research and development of innovative technologies can significantly enhance agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices. Developing cost-effective and efficient methods for waste utilization will further incentivize adoption and accelerate the transition to a circular economy.
Now, let's move on to a listicle of the benefits of agri-food waste recycling and valorization.
Listicle of Benefits of Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization
- Environmental Preservation: Agri-food waste recycling and valorization help reduce the amount of waste sent to landfill, minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and their impact on climate change.
- Resource Conservation: By transforming waste into valuable resources, agri-food waste recycling and valorization promote efficient resource utilization and reduce the need for extraction of new resources.
- Sustainable Energy Production: Waste-based energy generation through processes like anaerobic digestion and biomass conversion reduces reliance on fossil fuels and contributes to a more sustainable energy sector.
- Increased Food Security: Proper management of agri-food waste can lead to better food security by minimizing food loss, maximizing resource utilization, and redistributing surplus food to those in need.
- Cost Savings: Implementing agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices can lead to cost savings for businesses, as waste disposal and resource acquisition costs are reduced.
- Job Creation: The establishment of agri-food waste recycling and valorization facilities creates job opportunities in waste management, research and development, and related sectors.
- Positive Public Image: Companies and organizations that actively participate in waste reduction initiatives gain a positive reputation and are seen as responsible and environmentally conscious.
- Promotion of Circular Economy: Agri-food waste recycling and valorization are integral to the concept of a circular economy, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
- Soil Health Improvement: The use of compost derived from agri-food waste as a natural fertilizer enhances soil health by improving its structure, nutrient content, and water-holding capacity.
- Reduction in Water Pollution: Agri-food waste recycling and valorization methods that involve the treatment of waste can help reduce the release of pollutants into water bodies, contributing to water pollution prevention.
Now, let's move on to answering some common questions related to agri-food waste recycling and valorization.
Question & Answer
Q: Why is agri-food waste recycling important?
A: Agri-food waste recycling is important because it helps minimize wastage, reduces environmental impact, conserves resources, and contributes to a more sustainable and circular food system.
Q: What are the challenges associated with agri-food waste recycling?
A: Some challenges include the lack of awareness and infrastructure for waste collection and recycling, limited market demand for recycled products, and the need for technological advancements for efficient waste processing.
Q: How can individuals contribute to agri-food waste recycling?
A: Individuals can contribute to agri-food waste recycling by practicing composting, reducing food waste at home, supporting local food banks or organizations that redistribute surplus food, and actively participating in recycling initiatives in their communities.
Q: How does agri-food waste recycling contribute to sustainable development?
A: Agri-food waste recycling contributes to sustainable development by reducing waste generation, conserving resources, promoting renewable energy production, improving soil health, and fostering a more efficient and sustainable food system.
Q: What are the future prospects for agri-food waste recycling and valorization?
A: With increasing awareness of sustainability and the need to transition towards a circular economy, the future prospects for agri-food waste recycling and valorization are promising. Continued technological advancements and regulatory support will further accelerate the adoption of these practices.
Lastly, let's summarize the key points discussed in this article.
Summary of Agri-Food Waste Recycling and Valorization
Agri-food waste recycling and valorization are crucial for achieving a more sustainable and resource-efficient food system. By implementing practices such as composting, anaerobic digestion, biomass conversion, and food redistribution, valuable resources can be extracted from waste, reducing environmental impact and promoting a circular economy.
Collaboration, education, incentives, regulatory frameworks, and technological innovation are vital for the successful implementation of agri-food waste recycling and valorization practices. The benefits include environmental preservation, resource conservation, sustainable energy production, increased food security, cost savings, job creation, and promotion of a circular economy.
By actively participating in agri-food waste recycling and valorization, individuals, businesses, and policymakers can contribute to a more sustainable future, ensuring the well-being of both the planet and its inhabitants.
Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Waste Management From Reduction To Resource Recovery"