Agri-Food Traceability Systems For Supply Chain Transparency And Quality Assurance
The traceability of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana has gained significant traction in recent years, driven by the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. Blockchain's decentralized and transparent nature provides a promising solution to overcome various challenges faced by the agri-food industry, including fraud, counterfeiting, inefficient processes, and lack of consumer trust. This article aims to explore the potential of blockchain technology in enhancing the traceability of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana, presenting ideas, recommendations, and answering key questions surrounding its implementation.

What is blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a digital ledger that records and verifies transactions, allowing multiple parties to have access to the same information in a secure and immutable manner. It consists of blocks, which store data, and a chain that connects these blocks using cryptographic techniques. Each block contains a unique identifier (hash) and a reference to the previous block, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the data stored within the blockchain.
Ideas for implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain:
1. Enhancing transparency: Blockchain technology can provide a decentralized platform for participants in the agri-food supply chain to share information, ensuring transparency and visibility at each stage of the process. This transparency can help eliminate fraudulent activities, such as the mislabeling of products or the use of counterfeit ingredients.
2. Improving traceability: By recording each transaction on the blockchain, it becomes possible to trace the origin of products, including the source of raw materials, the manufacturing process, and the distribution network. This level of traceability is crucial in identifying the root cause of any quality or safety issues and facilitating targeted recalls if necessary.
3. Ensuring food safety: Blockchain technology can enable real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions during the transportation and storage of agri-food products. Any deviations from the predefined parameters can be instantly recorded on the blockchain, triggering alerts and ensuring timely actions to prevent spoilage or contamination.
4. Streamlining supply chain processes: By automating manual processes through smart contracts, blockchain technology can optimize various supply chain activities, including inventory management, order processing, and payments. This automation eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces paperwork, and enables faster and more efficient transactions.
5. Building consumer trust: With blockchain technology, consumers can have access to an immutable record of the entire journey of a product, including its origin, handling, and quality certifications. This transparency fosters trust between consumers and producers, allowing consumers to make informed choices about the products they purchase while encouraging ethical and sustainable practices in the agri-food industry.
Recommendations for implementing blockchain in the agri-food supply chain:
1. Collaborative approach: The successful implementation of blockchain technology in the agri-food supply chain requires collaboration among all stakeholders, including farmers, processors, distributors, regulators, and consumers. It is essential to establish trust, define common standards, and create a consortium that governs the blockchain network, ensuring its integrity and security.
2. Education and awareness: As blockchain technology is still relatively new, it is crucial to educate all participants in the agri-food supply chain about its benefits, functionalities, and potential challenges. Training programs, workshops, and awareness campaigns can help stakeholders understand how blockchain can be integrated into their existing processes and how it can drive positive change in the industry.
3. Scalability and interoperability: Given the complex and diverse nature of the agri-food supply chain, it is essential to ensure that the blockchain network is scalable and interoperable. This means that the technology should be able to handle a large volume of transactions, accommodate different types of data, and seamlessly integrate with existing systems and platforms used by participants in the supply chain.
4. Data privacy and security: Blockchain technology provides a high level of security through its decentralized architecture and cryptographic techniques. However, it is crucial to implement additional measures to protect sensitive data, such as personal information or trade secrets, from unauthorized access. This can involve encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance with data protection regulations.
5. Piloting and evaluation: Before implementing blockchain technology on a large scale, it is advisable to conduct pilot projects to assess its feasibility, scalability, and potential impact. Pilots can help identify challenges and opportunities specific to the agri-food industry in Ghana, allowing stakeholders to make informed decisions and fine-tune the implementation strategy accordingly.
Listicle of benefits of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain:
- Enhanced traceability and transparency
- Improved food safety and quality control
- Efficient inventory management and supply chain optimization
- Reduced fraud and counterfeiting
- Increased trust and consumer confidence
- Real-time monitoring of environmental conditions
- Streamlined payments and reduced transaction costs
- Promotion of ethical and sustainable practices
- Faster and more efficient recalls in case of emergencies
- Automation of manual processes through smart contracts
Question & Answer:
Q: How can blockchain technology prevent fraud in the agri-food supply chain?
A: Blockchain technology provides a decentralized and transparent platform that enables all participants in the supply chain to verify and validate each transaction. Any attempts to manipulate or alter the data stored on the blockchain would require the consensus of the majority of network participants, making fraudulent activities visible and practically impossible to execute without detection.
Q: Can blockchain technology help improve the efficiency of international trade in the agri-food industry?
A: Yes, blockchain technology can significantly enhance the efficiency of international trade in the agri-food industry. By providing a transparent and tamper-proof record of transactions, it eliminates the need for intermediaries, reduces paperwork and delays, and ensures timely payments and delivery. Additionally, blockchain's traceability features enable easy verification of compliance with international standards and regulations, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions.
Summary:
Blockchain technology holds great promise in revolutionizing the traceability of the agri-food supply chain in Ghana. The use of blockchain can enhance transparency, traceability, and trust among all stakeholders, leading to improved food safety, optimization of supply chain processes, and increased consumer confidence. However, successful implementation requires collaboration, education, scalability, data security, and pilot projects to evaluate feasibility and fine-tune the strategy. As Ghana's agri-food industry embraces blockchain technology, it has the potential to become a beacon of innovation and sustainability, setting new standards for the global agri-food supply chain. 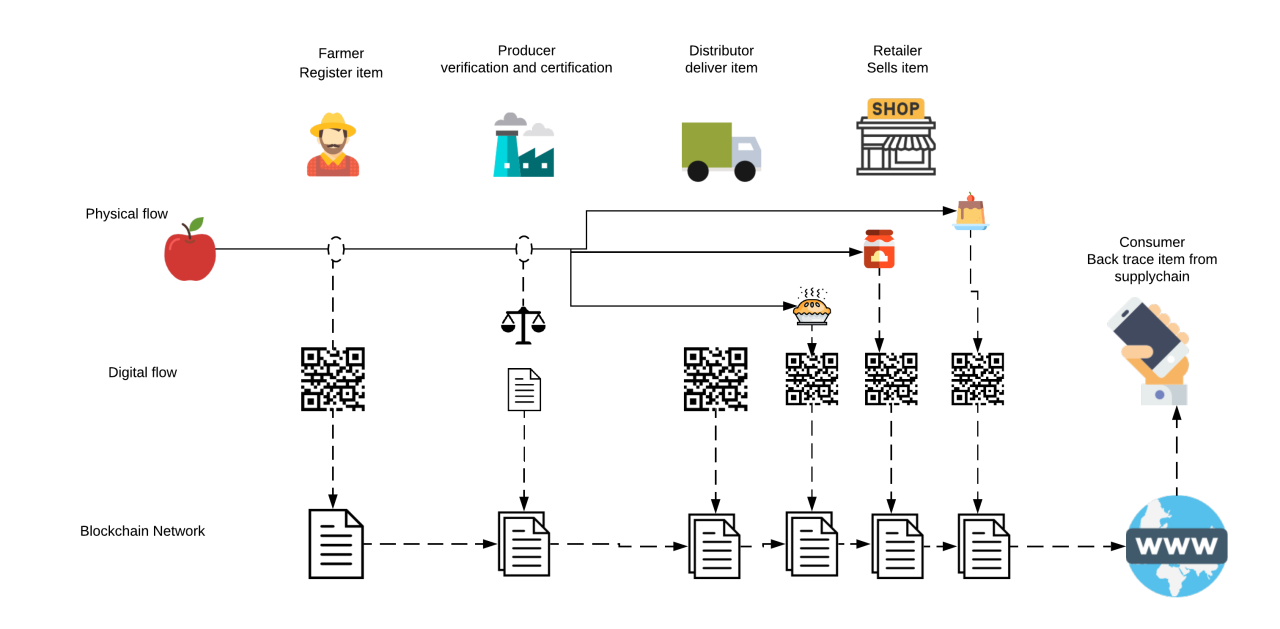
Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Traceability Systems For Supply Chain Transparency And Quality Assurance"