Agri-Food Waste Reduction Strategies For Sustainable Future
Recycling and Valorization of Agri-Food Waste
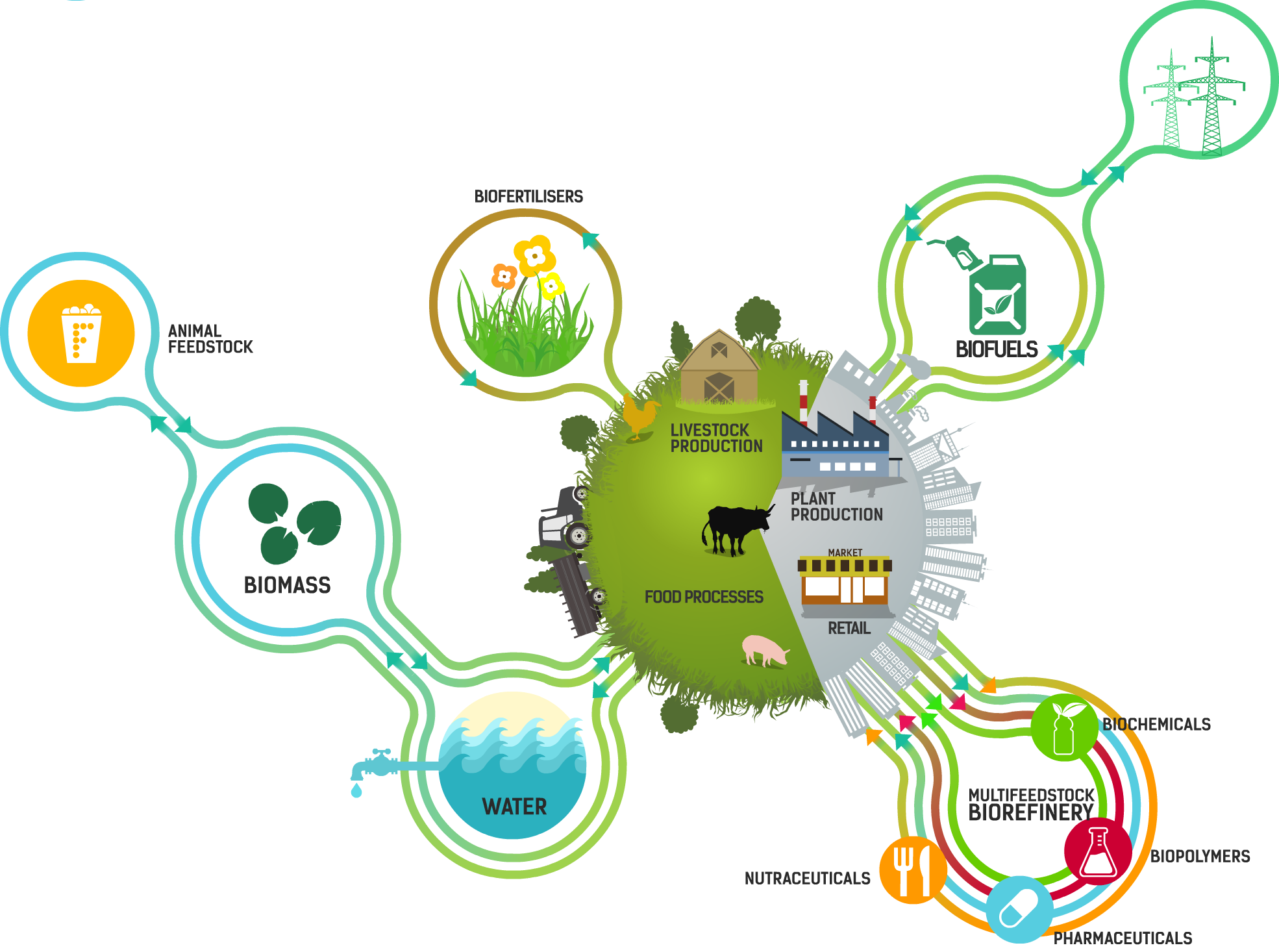
Food waste continues to be a critical issue around the world - a problem that affects not only our environment but also our economy and social well-being. In recent years, there has been a growing focus on recycling and valorization of agri-food waste as a means to address this problem. This article explores the various initiatives and strategies in place to tackle the challenge of agri-food waste, highlighting the importance of sustainable practices and innovation in creating a more circular economy.
What is Agri-Food Waste?
Agri-food waste refers to any organic material produced or derived from agricultural activities or the food and beverage industry that is discarded or considered to be of little or no value. This waste can include fruit and vegetable trimmings, leftover food, crop residues, and processing by-products. With the increasing global demand for food, the generation of agri-food waste has simultaneously risen, posing significant environmental and economic challenges.
Ideas For Recycling and Valorization of Agri-Food Waste
As awareness and concern for the environmental impact of food waste have grown, numerous innovative ideas and practices have emerged to recycle and valorize agri-food waste. These initiatives aim to reduce waste, maximize resource efficiency, and create sustainable solutions. Here are some of the key ideas and strategies being implemented:
1. Composting: Composting is a natural method that decomposes organic waste into nutrient-rich soil. By turning agri-food waste into compost, it can be used as an environmentally friendly alternative to chemical fertilizers, promoting soil health and reducing the need for synthetic additives.
2. Anaerobic Digestion: Anaerobic digestion is a process that breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas and nutrient-rich digestate. Biogas can be used as a renewable energy source, while the digestate can be utilized as a bio-fertilizer, closing the loop and minimizing waste in the agri-food sector.
3. Food Recovery and Redistribution: Food recovery programs involve collecting surplus food from farms, food processors, and retailers that would otherwise go to waste, and redistributing it to those in need. This approach not only prevents food waste but also helps address food insecurity and hunger.
4. Bioplastics and Biofuels: Agri-food waste can be utilized to produce bioplastics and biofuels, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional petroleum-based products. Through innovative technologies, waste can be transformed into raw materials for these eco-friendly products, reducing dependence on finite fossil fuels and minimizing carbon emissions.
Recommendations For Effective Waste Management
To optimize waste management practices and promote a circular economy, it is essential to implement the following recommendations:
1. Collaborative Partnerships: Foster collaboration between stakeholders across the agri-food value chain, including farmers, processors, retailers, and waste management companies, to establish efficient systems for waste separation, collection, and treatment.
2. Awareness and Education: Raise awareness among consumers, businesses, and policymakers about the importance of reducing, recycling, and valorizing agri-food waste. Educate individuals and organizations on practical ways to implement waste reduction strategies in their daily lives and operations.
3. Research and Innovation: Invest in research and development to identify new technologies and solutions for maximizing the value of agri-food waste. Support startups and entrepreneurs working on innovative projects that contribute to waste reduction and resource efficiency.
Listicle of Success Stories
Check out these inspiring success stories of recycling and valorization of agri-food waste from around the world:
- 1. The Winnow System: Winnow has developed smart technology that helps commercial kitchens reduce food waste. Their system uses artificial intelligence to analyze and measure food waste, providing real-time data and insights to help chefs and kitchen staff optimize their production processes.
- 2. Agrocycle: Agrocycle is an EU-funded project that aims to demonstrate innovative ways to valorize the by-products and waste generated by the agri-food industry. Through collaboration with a wide range of stakeholders, Agrocycle explores the potential of turning waste into valuable resources, such as biogas, biofertilizers, and high-value compounds.
- 3. Imperfect Foods: Imperfect Foods is an online grocer that rescues surplus and "imperfect" produce from farms and delivers it directly to consumers' doors. By embracing these "ugly" fruits and vegetables, Imperfect Foods helps reduce food waste and promotes a more sustainable food system.
- 4. Too Good To Go: Too Good To Go is a mobile app that connects consumers with local restaurants, cafes, and bakeries to rescue their surplus food at the end of the day. By purchasing "Magic Bags" at a discounted price, users can enjoy a variety of delicious meals while combating food waste.
- 5. Loop: Loop is a circular shopping platform that enables consumers to purchase common household products in reusable packaging. By partnering with various brands, Loop aims to eliminate single-use packaging and establish a closed-loop system, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Question & Answer
Q: How can individuals contribute to reducing agri-food waste?
A: Individuals can make a significant impact by adopting simple practices, such as planning meals, properly storing food, and composting kitchen scraps. Additionally, supporting local farmers and businesses that prioritize sustainable practices helps create a demand for responsible food production.
Q: What role can policymakers play in addressing agri-food waste?
A: Policymakers have the power to implement regulations and incentives that promote waste reduction, encourage sustainable packaging, and support initiatives for recycling and valorization of agri-food waste. By prioritizing these actions, policymakers can contribute to building a sustainable and resilient food system.
Q: Can recycling and valorization of agri-food waste help tackle climate change?
A: Absolutely! By recycling and valorizing agri-food waste, we reduce the emissions of potent greenhouse gases that would otherwise be released during the decomposition of organic waste in landfills. Additionally, when waste is transformed into renewable energy or valuable products, it reduces the need for fossil fuels or virgin raw materials, further mitigating climate change impacts.
Summary of Recycling and Valorization of Agri-Food Waste
Recycling and valorization of agri-food waste present a tremendous opportunity to address the pressing issue of food waste while creating a more sustainable and circular economy. By embracing innovative technologies, fostering collaboration, and promoting responsible consumption and production, we can reduce waste generation, conserve resources, and alleviate the strain on our environment and global food systems. Together, let's work towards a future where agri-food waste becomes a valuable resource rather than a burden.
...
Post a Comment for "Agri-Food Waste Reduction Strategies For Sustainable Future"